Analysis of the direct economic impact of smoking-related hospitalizations in Italy
- PMID: 38832050
- PMCID: PMC11145629
- DOI: 10.18332/tid/188111
Analysis of the direct economic impact of smoking-related hospitalizations in Italy
Abstract
Introduction: Tobacco-related diseases have a substantial economic impact in terms of medical expenses, loss of productivity, and premature death. Tobacco use is estimated to be responsible for more than 90000 deaths each year in Italy. We aimed to evaluate the annual direct economic impact on the National Health System of hospitalizations attributable to tobacco smoking in Italy.
Methods: We analyzed data from all the hospitalizations of patients aged ≥30 years that occurred in Italy for 12 selected tobacco-related diseases, during 2018. These diseases included oropharyngeal cancer, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, laryngeal cancer, ischemic heart disease, stroke, diseases of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries, pneumonia and influenza, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. We obtained information on 984322 hospital discharge records, including each hospitalization's direct costs. Using relative risk estimates from the scientific literature, we computed the population attributable fraction for various tobacco-related diseases to estimate the economic impact attributable to tobacco smoking.
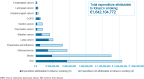
Results: One-third of all hospitalizations occurred in 2018 in Italy among people aged ≥30 years for 12 tobacco-related diseases were found to be attributable to smoking, accounting for a total cost of €1.64 billion. Among the diseases considered, those with the highest expenditures attributable to tobacco smoking were ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and lung cancer, accounting for €556 million, €290 million, and €229 million, respectively.
Conclusions: Tobacco has a substantial economic impact in Italy, accounting for around 6% of the total cost of hospitalizations in 2018. This figure is expected to be largely underestimated due to several conservative assumptions adopted in the statistical analyses. It is imperative to prioritize comprehensive tobacco control measures to counteract the huge healthcare costs due to tobacco smoking.
Keywords: Italy; burden of disease; cost of illness; smoking; tobacco.
© 2024 Possenti I. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest and none was reported.
Figures
References
-
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (US) Office on Smoking and Health . The Health Consequences of Smoking—50 Years of Progress: A Report of the Surgeon General. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US; ); 2014. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute . Harms of Cigarette Smoking and Health Benefits of Quitting. December 19, 2017. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/tobacco/cessa...
-
- World Health Organization . WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic 2021: addressing new and emerging products. July 27, 2021. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240032095
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources