Quantitative and qualitative analysis of metallic ion release of orthodontic brackets in three different pH conditions - An invitro study
- PMID: 38832295
- PMCID: PMC11144748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.05.001
Quantitative and qualitative analysis of metallic ion release of orthodontic brackets in three different pH conditions - An invitro study
Abstract
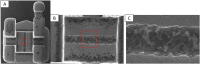
Background: Fluoridated mouth rinses improve anti-cariogenic environment but decrease oral pH below critical value, affecting orthodontic bracket surface topography and causing corrosive changes over prolonged use. This invitro study aimed to quantitatively and qualitatively assess the surface topography and metallic ion release of the stainless steel (SS) brackets at varying acidic and alkaline pH.
Materials and methods: Forty unused SS brackets were divided into four groups (Group A, B, C, D) and immersed for 48- hours in solutions of artificial saliva and sodium fluoride (0.2 %) mouth rinse at varying pH of 5.5,6.7,7 and 8. The surface morphologic changes were analyzed under scanning electron microscope (SEM) at 50×, 150×, and 500× magnification. The changes in slot area were scored using the customized scale. The Energy Dispersive Xray Spectroscopy Analysis (EDAX) was used to estimate the probed elements' atomic and weight percentage.
Results: The mean score of the scale was 3.4 for the brackets immersed in the acidic solution which was statistically significant (p = 0.00)and for alkaline and neutral solutions (p = 0.00). Chromium was found to be significantly higher in the alkaline solution (p = 0.016) followed by the neutral solution. Carbon was found excess in acidic solution than the neutral and alkaline solution.
Conclusion: Quantitative and qualitative analysis of the ion release in stainless steel brackets using SEM and EDAX revealed the corrosive effect of fluoride ion causing maximum surface changes in acidic medium and chromium release in alkaline pH.
Keywords: Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy; Scanning electron microscope; Surface topography.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

