Introduction of the Capsules environment to support further growth of the SBGrid structural biology software collection
- PMID: 38832828
- PMCID: PMC11154594
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798324004881
Introduction of the Capsules environment to support further growth of the SBGrid structural biology software collection
Abstract
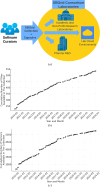
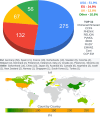
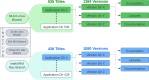
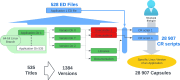
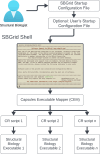
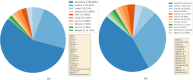
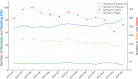
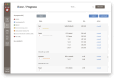
The expansive scientific software ecosystem, characterized by millions of titles across various platforms and formats, poses significant challenges in maintaining reproducibility and provenance in scientific research. The diversity of independently developed applications, evolving versions and heterogeneous components highlights the need for rigorous methodologies to navigate these complexities. In response to these challenges, the SBGrid team builds, installs and configures over 530 specialized software applications for use in the on-premises and cloud-based computing environments of SBGrid Consortium members. To address the intricacies of supporting this diverse application collection, the team has developed the Capsule Software Execution Environment, generally referred to as Capsules. Capsules rely on a collection of programmatically generated bash scripts that work together to isolate the runtime environment of one application from all other applications, thereby providing a transparent cross-platform solution without requiring specialized tools or elevated account privileges for researchers. Capsules facilitate modular, secure software distribution while maintaining a centralized, conflict-free environment. The SBGrid platform, which combines Capsules with the SBGrid collection of structural biology applications, aligns with FAIR goals by enhancing the findability, accessibility, interoperability and reusability of scientific software, ensuring seamless functionality across diverse computing environments. Its adaptability enables application beyond structural biology into other scientific fields.
Keywords: Capsule Software Execution Environment; FAIR principles; SBGrid; high-performance computing; scientific software; structural biology; structure determination.
open access.
Figures
References
-
- Agirre, J., Atanasova, M., Bagdonas, H., Ballard, C. B., Baslé, A., Beilsten-Edmands, J., Borges, R. J., Brown, D. G., Burgos-Mármol, J. J., Berrisford, J. M., Bond, P. S., Caballero, I., Catapano, L., Chojnowski, G., Cook, A. G., Cowtan, K. D., Croll, T. I., Debreczeni, J. É., Devenish, N. E., Dodson, E. J., Drevon, T. R., Emsley, P., Evans, G., Evans, P. R., Fando, M., Foadi, J., Fuentes-Montero, L., Garman, E. F., Gerstel, M., Gildea, R. J., Hatti, K., Hekkelman, M. L., Heuser, P., Hoh, S. W., Hough, M. A., Jenkins, H. T., Jiménez, E., Joosten, R. P., Keegan, R. M., Keep, N., Krissinel, E. B., Kolenko, P., Kovalevskiy, O., Lamzin, V. S., Lawson, D. M., Lebedev, A. A., Leslie, A. G. W., Lohkamp, B., Long, F., Malý, M., McCoy, A. J., McNicholas, S. J., Medina, A., Millán, C., Murray, J. W., Murshudov, G. N., Nicholls, R. A., Noble, M. E. M., Oeffner, R., Pannu, N. S., Parkhurst, J. M., Pearce, N., Pereira, J., Perrakis, A., Powell, H. R., Read, R. J., Rigden, D. J., Rochira, W., Sammito, M., Sánchez Rodríguez, F., Sheldrick, G. M., Shelley, K. L., Simkovic, F., Simpkin, A. J., Skubak, P., Sobolev, E., Steiner, R. A., Stevenson, K., Tews, I., Thomas, J. M. H., Thorn, A., Valls, J. T., Uski, V., Usón, I., Vagin, A., Velankar, S., Vollmar, M., Walden, H., Waterman, D., Wilson, K. S., Winn, M. D., Winter, G., Wojdyr, M. & Yamashita, K. (2023). Acta Cryst. D79, 449–461.
-
- Babinet, E. & Ramanathan, R. (2008). Agile 2008 Conference, pp. 401–406. Piscataway: IEEE.
-
- Baker, M. (2016). Nature, 533, 452–454. - PubMed
-
- Bakshi, K. (2017). 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, pp. 1–8. Piscataway: IEEE.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

