Glucagon-like peptide-1 increases heart rate by a direct action on the sinus node
- PMID: 38832935
- PMCID: PMC11472427
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvae120
Glucagon-like peptide-1 increases heart rate by a direct action on the sinus node
Abstract
Aims: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are increasingly used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. Albeit cardiovascular outcomes generally improve, treatment with GLP-1 RAs is associated with increased heart rate, the mechanism of which is unclear.
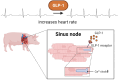
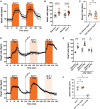
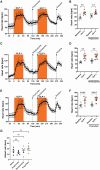
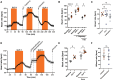
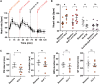
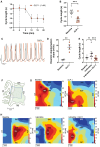
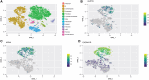
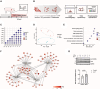
Methods and results: We employed a large animal model, the female landrace pig, and used multiple in vivo and ex vivo approaches including pharmacological challenges, electrophysiology, and high-resolution mass spectrometry to explore how GLP-1 elicits an increase in heart rate. In anaesthetized pigs, neither cervical vagotomy, adrenergic blockers (alpha, beta, or combined alpha-beta blockade), ganglionic blockade (hexamethonium), nor inhibition of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels (ivabradine) abolished the marked chronotropic effect of GLP-1. GLP-1 administration to isolated perfused pig hearts also increased heart rate, which was abolished by GLP-1 receptor blockade. Electrophysiological characterization of GLP-1 effects in vivo and in isolated perfused hearts localized electrical modulation to the atria and conduction system. In isolated sinus nodes, GLP-1 administration shortened the action potential cycle length of pacemaker cells and shifted the site of earliest activation. The effect was independent of HCN blockade. Collectively, these data support a direct effect of GLP-1 on GLP-1 receptors within the heart. Consistently, single nucleus RNA sequencing showed GLP-1 receptor expression in porcine pacemaker cells. Quantitative phosphoproteomics analyses of sinus node samples revealed that GLP-1 administration leads to phosphorylation changes of calcium cycling proteins of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, known to regulate heart rate.
Conclusion: GLP-1 has direct chronotropic effects on the heart mediated by GLP-1 receptors in pacemaker cells of the sinus node, inducing changes in action potential morphology and the leading pacemaker site through a calcium signalling response characterized by PKA-dependent phosphorylation of Ca2+ cycling proteins involved in pacemaking. Targeting the pacemaker calcium clock may be a strategy to lower heart rate in people treated with GLP-1 RAs.
Keywords: Calcium clock; Calcium signalling; Chronotropic; GLP-1; Glucagon-like peptide 1; Heart rate; Pacemaker; Sinus node.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: J.J.H. has been on advisory boards for Novo Nordisk. The other authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
New insights into the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on heart rate and sinoatrial node function.Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Oct 14;120(12):1367-1368. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae150. Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39028688 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sattar N, Lee MMY, Kristensen SL, Branch KRH, Prato D, Khurmi S, Lam NS, Lopes CSP, McMurray RD, Pratley JJV, Rosenstock RE, Gerstein J, Gerstein HC. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2021;9:653–662. - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, Probstfield J, Riesmeyer JS, Riddle MC, Ryden L, Xavier D, Atisso CM, Dyal L, Hall S, Rao-Melacini P, Wong G, Avezum A, Basile J, Chung N, Conget I, Cushman WC, Franek E, Hancu N, Hanefeld M, Holt S, Jansky P, Keltai M, Lanas F, Leiter LA, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Cardona Munoz EG, Pirags V, Pogosova N, Raubenheimer PJ, Shaw JE, Sheu WH, Temelkova-Kurktschiev T, REWIND Investigators . Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019;394:121–130. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez AF, Green JB, Janmohamed S, D'Agostino RB, Sr., Granger CB, Jones NP, Leiter LA, Rosenberg AE, Sigmon KN, Somerville MC, Thorpe KM, McMurray JJV, Del Prato S; Harmony Outcomes c, investigators . . Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018;392:1519–1529. - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, Thompson VP, Lokhnygina Y, Buse JB, Chan JC, Choi J, Gustavson SM, Iqbal N, Maggioni AP, Marso SP, Ohman P, Pagidipati NJ, Poulter N, Ramachandran A, Zinman B, Hernandez AF, EXSCEL Study Group . Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1228–1239. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Husain M, Birkenfeld AL, Donsmark M, Dungan K, Eliaschewitz FG, Franco DR, Jeppesen OK, Lingvay I, Mosenzon O, Pedersen SD, Tack CJ, Thomsen M, Vilsboll T, Warren ML, Bain SC, Investigators P. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2019;381:841–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

