A survey of isatin hybrids and their biological properties
- PMID: 38833124
- PMCID: PMC11909063
- DOI: 10.1007/s11030-024-10883-z
A survey of isatin hybrids and their biological properties
Abstract
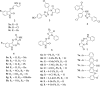
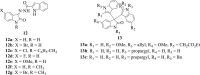
The emergence of diverse infections worldwide, which is a serious global threat to human existence, necessitates the urgent development of novel therapeutic candidates that can combat these diseases with efficacy. Molecular hybridization has been established as an efficient technique in designing bioactive molecules capable of fighting infections. Isatin, a core nucleus of an array of compounds with diverse biological properties can be modified at different positions leading to the creation of novel drug targets, is an active area of medicinal chemistry. This review containing published articles from 2005 to 2022 highlights isatin hybrids which have been synthesized and reported in the literature alongside a discussion on their biological properties. The enriched structure-activity relationship studies discussed provides insights for the rational design of novel isatin hybrids with tailored biological properties as effective therapeutic candidates inspired by nature.
Keywords: Biological properties; Isatin hybrids; Molecular hybridization; Pharmacophore; Structure–activity relationship.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
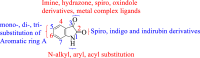


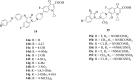
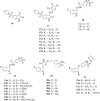

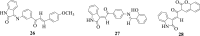




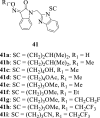






Similar articles
-
Indole/isatin-containing hybrids as potential antibacterial agents.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020 Oct;353(10):e2000143. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202000143. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020. PMID: 32667714 Review.
-
Moxifloxacin-isatin Hybrids Tethered by 1,2,3-triazole and their Anticancer Activities.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(16):1461-1467. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200128144825. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31994464
-
Isatin-azole hybrids and their anticancer activities.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020 Jan;353(1):e1900272. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201900272. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020. PMID: 31691360 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Diverse Spectrum Activity of 1,2,3-Triazole-linked Isatin Hybrids.Chem Biodivers. 2024 Apr;21(4):e202301612. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202301612. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38332679 Review.
-
A Mini Review on Pharmacological Significance of Isatin-1,2,3-Triazole Hybrids.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(10):833-847. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230202160925. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36733194 Review.
Cited by
-
Isatin Bis-Imidathiazole Hybrids Identified as FtsZ Inhibitors with On-Target Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;13(10):992. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100992. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452258 Free PMC article.
-
From Structure to Function: Isatin Derivatives as a Promising Class of Antiviral Agents.Curr Drug Targets. 2025;26(7):470-488. doi: 10.2174/0113894501352560250115054156. Curr Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39878104 Review.
-
In Vitro Enzymatic and Computational Assessments of Pyrazole-Isatin and Pyrazole-Indole Conjugates as Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Arthritic, and Anti-Inflammatory Agents.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 23;17(3):293. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030293. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142957 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Activity Evaluation of Phenolic Isatin-3-Hydrazones Containing a Quaternary Ammonium Center of Various Structures.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11130. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011130. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456912 Free PMC article.
-
Novel isatin conjugates endowed with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties: design, synthesis and biological evaluation.Future Med Chem. 2025 Jan;17(1):59-73. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2437981. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39676545
References
-
- Medvedev A, Buneeva O, Gnedenko O, Ershov P, Ivanov A (2018) Isatin, an endogenous nonpeptide biofactor; a review of its molecular targets, mechanisms of actions, and their biomedical implications. BioFactors 44:95–108 - PubMed
-
- Sagnou M, Mavroidi B, Kaminari A, Boukos N, Pelecanou M (2020) Novel isatin thiosemicarbazone derivatives as potent inhibitors of β-amyloid peptide aggregation and toxicity. ACS Chem Neurosci 11:2266–2276 - PubMed
-
- Rezki N, Almehmadi MA, Ihmaid S, Shehata AM, Omar AM, Ahmed HEA, Aouad MA (2020) Novel scaffold hopping of potent benzothiazole and isatin analogues linked to 1,2,3-triazole fragment that mimic quinazoline epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors; synthesis, antitumor and mechanistic analyses. Bioorg Chem 103:104133 - PubMed
-
- Pakravan P, Kashanian S, Khodaei MM, Harding FA (2013) Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of isatin and its derivatives; from structure to activity. Pharmacol Rep 65:313–335 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

