Two nomograms constructed for predicting the efficacy and prognosis of advanced non‑small cell lung cancer patients treated with anti‑PD‑1 inhibitors based on the absolute counts of lymphocyte subsets
- PMID: 38833153
- PMCID: PMC11150349
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-024-03738-x
Two nomograms constructed for predicting the efficacy and prognosis of advanced non‑small cell lung cancer patients treated with anti‑PD‑1 inhibitors based on the absolute counts of lymphocyte subsets
Abstract
Background: Patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are at risk of considerable adverse events, and the ongoing struggle is to accurately identify the subset of patients who will benefit. Lymphocyte subsets play a pivotal role in the antitumor response, this study attempted to combine the absolute counts of lymphocyte subsets (ACLS) with the clinicopathological parameters to construct nomograms to accurately predict the prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (aNSCLC) patients treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors.
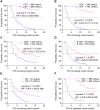
Methods: This retrospective study included a training cohort (n = 200) and validation cohort (n = 100) with aNSCLC patients treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors. Logistic and Cox regression were conducted to identify factors associated with efficacy and progression-free survival (PFS) respectively. Nomograms were built based on independent influencing factors, and assessed by the concordance index (C-index), calibration curve and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
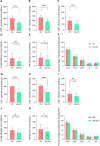
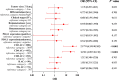
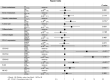
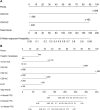
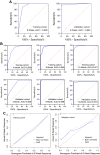
Result: In training cohort, lower baseline absolute counts of CD3+ (P < 0.001) and CD4+ (P < 0.001) were associated with for poorer efficacy. Hepatic metastases (P = 0.019) and lower baseline absolute counts of CD3+ (P < 0.001), CD4+ (P < 0.001), CD8+ (P < 0.001), and B cells (P = 0.042) were associated with shorter PFS. Two nomograms to predict efficacy at 6-week after treatment and PFS at 4-, 8- and 12-months were constructed, and validated in validation cohort. The area under the ROC curve (AUC-ROC) of nomogram to predict response was 0.908 in training cohort and 0.984 in validation cohort. The C-index of nomogram to predict PFS was 0.825 in training cohort and 0.832 in validation cohort. AUC-ROC illustrated the nomograms had excellent discriminative ability. Calibration curves showed a superior consistence between the nomogram predicted probability and actual observation.
Conclusion: We constructed two nomogram based on ACLS to help clinicians screen of patients with possible benefit and make individualized treatment decisions by accurately predicting efficacy and PFS for advanced NSCLC patient treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Absolute count; Anti-PD-1inhibitor; Lymphocyte subsets; Nomogram; Non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A clinical nomogram based on absolute count of lymphocyte subsets for predicting overall survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jan;114:109391. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109391. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36508919
-
Development of nomograms to predict therapeutic response and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with anti-PD-1 antibody.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Feb;70(2):533-546. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02710-9. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 32852602 Free PMC article.
-
New biomarkers exploration and nomogram construction of prognostic and immune-related adverse events of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors.Respir Res. 2023 Feb 27;24(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02370-0. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 36849947 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a lung immune prognostic index-based nomogram model for predicting overall survival and immune-related adverse events in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with sintilimab.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1569689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1569689. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406139 Free PMC article.
-
The systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) predicts survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immunotherapy and the construction of a nomogram model.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1516737. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1516737. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39776905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dynamic monitoring of lymphocyte subsets at different disease stages can predict the prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia especially in complete remission status.Sci Rep. 2025 May 17;15(1):17128. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01600-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40382411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amrein MA, Bührer ED, Amrein ML, Li Q, Rothschild S et al (2021) Chemotherapy negatively impacts the tumor immune microenvironment in NSCLC: an analysis of pre- and post-treatment biopsies in the multi-center SAKK19/09 study. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70:405–415. 10.1007/s00262-020-02688-4 10.1007/s00262-020-02688-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

