Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Olanzapine: Effects of Clinical Factors on Plasma Concentrations in Psychiatric Patients
- PMID: 38833576
- PMCID: PMC11554250
- DOI: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000001227
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Olanzapine: Effects of Clinical Factors on Plasma Concentrations in Psychiatric Patients
Abstract
Background: Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is strongly recommended for olanzapine due to its high pharmacokinetic variability. This study aimed to investigate the impact of various clinical factors on olanzapine plasma concentrations in patients with psychiatric disorders.
Methods: The study used TDM data from the PsyMetab cohort, including 547 daily dose-normalized, steady-state, olanzapine plasma concentrations (C:D ratios) from 248 patients. Both intrinsic factors (eg, sex, age, body weight) and extrinsic factors (eg, smoking status, comedications, hospitalization) were examined. Univariate and multivariable, linear, mixed-effects models were employed, with a stepwise selection procedure based on Akaike information criterion to identify the relevant covariates.
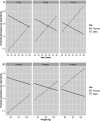
Results: In the multivariable model (based on 440 observations with a complete data set), several significant findings emerged. Olanzapine C:D ratios were significantly lower in smokers (β = -0.65, P < 0.001), valproate users (β = -0.53, P = 0.002), and inpatients (β = -0.20, P = 0.025). Furthermore, the C:D ratios decreased significantly as the time since the last dose increased (β = -0.040, P < 0.001). The male sex had a significant main effect on olanzapine C:D ratios (β = -2.80, P < 0.001), with significant interactions with age (β = 0.025, P < 0.001) and body weight (β = 0.017, P = 0.011). The selected covariates explained 30.3% of the variation in C:D ratios, with smoking status accounting for 7.7% and sex contributing 6.9%. The overall variation explained by both the fixed and random parts of the model was 67.4%. The model facilitated the prediction of olanzapine C:D ratios based on sex, age, and body weight.
Conclusions: The clinical factors examined in this study, including sex, age, body weight, smoking status, and valproate comedication, remarkably influence olanzapine C:D ratios. Considering these factors, in addition to TDM and the clinical situation, could be important for dose adjustment.
Keywords: clinical factors; olanzapine; plasma concentrations; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Over the past 3 years, N. Ansermot has been awarded honoraria for a conference by Sysmex Suisse AG. S. Crettol has earned honoraria for conducting CME courses on behalf of Forum pour la formation médicale, Barr, Switzerland, and has provided consultancy services for the Swiss Health Observatory (Obsan) under the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health. F. Vandenberghe has received honoraria for delivering CME courses through Forum pour la formation médicale, Barr, Switzerland, in addition to CME courses for the Swiss Association of Public Health Administration and for a conference organized by Sysmex Suisse AG. C. B. Eap was honored with honoraria for his participation in conferences sponsored by Forum pour la formation médicale, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Sandoz, Servier, Sunovion, Sysmex Suisse AG, Takeda, Vifor-Pharma, and Zeller within the same time frame. No declarations were made by the remaining authors. The authors affirm no conflicts of interest concerning the content of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Retrospective Analysis of Steady-State Olanzapine Concentrations in Chinese Patients Using Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: Effects of Valproate and Other Factors.Ther Drug Monit. 2020 Aug;42(4):636-642. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000738. Ther Drug Monit. 2020. PMID: 32039940
-
Effects of age and sex on olanzapine plasma concentrations.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2005 Dec;25(6):570-4. doi: 10.1097/01.jcp.0000185427.08268.db. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16282840
-
The Impact of Smoking, Sex, Infection, and Comedication Administration on Oral Olanzapine: A Population Pharmacokinetic Model in Chinese Psychiatric Patients.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2021 May;46(3):353-371. doi: 10.1007/s13318-021-00673-5. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2021. PMID: 33677821
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of atypical antipsychotics: a critical review of the relationship between plasma concentrations and clinical response.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(5):359-88. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200746050-00001. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007. PMID: 17465637 Review.
-
[Olanzapine: pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic drug monitoring].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2001 Nov;69(11):510-7. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-18381. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2001. PMID: 11704898 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Do women need a change in dose of prescription drugs with onset of menopause? Time to find out.BMC Med. 2025 Jul 7;23(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04253-1. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40624672 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Drugs@FDA search. Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/. Accessed August 31, 2022.
-
- Kantrowitz JT, Citrome L. Olanzapine: review of safety 2008. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2008;7:761–769. - PubMed
-
- Callaghan JT, Bergstrom RF, Ptak LR, et al. . Olanzapine. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;37:177–193. - PubMed
-
- Bhana N, Foster RH, Olney R, et al. . Olanzapine: an updated review of its use in the management of schizophrenia. Drugs. 2001;61:111–161. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

