Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Standard of Care for Previously Treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Final Analysis of the Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III LEAP-017 Study
- PMID: 38833658
- PMCID: PMC11328923
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02736
Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Standard of Care for Previously Treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Final Analysis of the Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III LEAP-017 Study
Abstract
Purpose: Treatment options are limited for patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). In the LEAP-017 study, we evaluate whether lenvatinib in combination with pembrolizumab improves outcomes compared with standard of care (SOC) in previously treated mismatch repair proficient or not microsatellite instability high (pMMR or not MSI-H) mCRC.
Methods: In this international, multicenter, randomized, controlled, open-label, phase III study, eligible patients age 18 years and older with unresectable, pMMR or not MSI-H mCRC, that had progressed on or after, or could not tolerate, standard treatment, were randomly assigned 1:1 to lenvatinib 20 mg orally once daily plus pembrolizumab 400 mg intravenously once every 6 weeks or investigator's choice of regorafenib or trifluridine/tipiracil (SOC). Randomization was stratified by presence or absence of liver metastases. The primary end point was overall survival (OS). LEAP-017 is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04776148), and has completed recruitment.
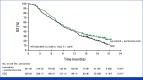
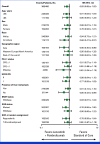
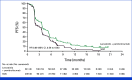
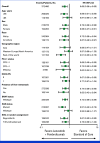
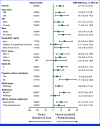
Results: Between April 8, 2021, and December 21, 2021, 480 patients were randomly assigned to lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab (n = 241) or SOC (n = 239). At final analysis (median follow-up of 18.6 months [IQR, 3.9]), median OS with lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus SOC was 9.8 versus 9.3 months (hazard ratio [HR], 0.83 [95% CI, 0.68 to 1.02]; P = .0379; prespecified threshold P = .0214). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 58.4% (lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab) versus 42.1% (SOC) of patients. Two participants died due to treatment-related adverse events, both in the lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab arm.
Conclusion: In patients with pMMR or not MSI-H mCRC that had progressed on previous therapy, there was no statistically significant improvement in OS after lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab treatment versus SOC. No new safety signals were observed.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER): All Cancer Sites Combined Recent Trends in SEER Age-Adjusted Incidence Rates, 2000-2021. https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) : Colon Cancer. Version 3. 2022. 2022. https://NCCN.org
-
- Cervantes A, Adam R, Roselló S, et al. : Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 34:10-32, 2023 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

