Real-world outcomes with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC: interim analysis of overall survival from PACIFIC-R
- PMID: 38833971
- PMCID: PMC11179087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103464
Real-world outcomes with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC: interim analysis of overall survival from PACIFIC-R
Abstract
Background: Based on the findings of the PACIFIC trial, consolidation durvalumab following platinum-based chemoradiotherapy (CRT) is a global standard of care for patients with unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). An earlier analysis from the ongoing PACIFIC-R study (NCT03798535) demonstrated the effectiveness of this regimen in terms of progression-free survival (PFS). Here, we report the first planned overall survival (OS) analysis.
Patients and methods: PACIFIC-R is an observational/non-interventional, retrospective study of patients with unresectable, stage III NSCLC who started durvalumab (10 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks) within an AstraZeneca-initiated early access program between September 2017 and December 2018. Primary endpoints are OS and investigator-assessed PFS, estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
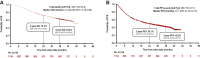
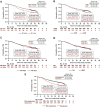
Results: By 30 November 2021, the full analysis set included 1154 participants from 10 countries (median follow-up in censored patients: 38.7 months). Median OS was not reached, and the 3-year OS rate was 63.2% (95% confidence interval 60.3% to 65.9%). Three-year OS rates were numerically higher among patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression on ≥1% versus <1% of tumor cells (TCs; 67.0% versus 54.4%) and patients who received concurrent CRT (cCRT) versus sequential CRT (sCRT) (64.8% versus 57.9%).
Conclusions: PACIFIC-R data continue to provide evidence for the effectiveness of consolidation durvalumab after CRT in a large, diverse, real-world population. Better outcomes were observed among patients with PD-L1 TCs ≥1% and patients who received cCRT. Nevertheless, encouraging outcomes were still observed among patients with TCs <1% and patients who received sCRT, supporting use of consolidation durvalumab in a broad population of patients with unresectable, stage III NSCLC.
Keywords: PD-L1; durvalumab; immunotherapy; locally advanced NSCLC; real-world evidence.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Walters S., Maringe C., Coleman M.P., et al. Lung cancer survival and stage at diagnosis in Australia, Canada, Denmark, Norway, Sweden and the UK: a population-based study, 2004-2007. Thorax. 2013;68(6):551–564. - PubMed
-
- Antonia S.J., Villegas A., Daniel D., et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(24):2342–2350. - PubMed
-
- Antonia S.J., Villegas A., Daniel D., et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1919–1929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

