Prevalence of depression and its associated factors among Ethiopian students: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38834322
- PMCID: PMC11163678
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076580
Prevalence of depression and its associated factors among Ethiopian students: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study is to estimate the overall pooled prevalence of depression and its associated factors among high school, college and university students in Ethiopia.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data sources: PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, Science Direct, African Journal Online and Google Scholar. The primary articles were searched from 2 April 2023 to 11 May 2023.
Eligibility criteria: Observational studies such as cross-sectional, case-control and cohort studies that reported the prevalence and associated factors of depression among students in Ethiopia were included. Both published and unpublished primary studies were included in this review.
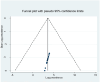
Data extraction and synthesis: Two authors independently extracted all the important data using a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet and exported it to Stata V.14 for analysis. The statistical heterogeneity among the included articles was assessed by the I2 statistics test. Publication bias was checked using the funnel plot and Egger's regression test.
Results: A total of 17 primary studies with 8798 study participants were included in the current study to estimate the combined prevalence of depression. The pooled prevalence of depression among Ethiopian students was 35.52% with a 95% CI (30.54% to 40.51%). Subgroup analysis showed that the pooled prevalence of depression was higher in Addis Ababa, which was 40.43%, with a 95% CI (28.02% to 52.83%). Female sex, first-year educational level, family history of mental illness, alcohol drinking and parental neglect were significantly associated with depression in this study.
Conclusion: In this review, the overall pooled prevalence of depression among students in Ethiopia was high compared with the general population. Therefore, it is necessary to make more efforts to provide mental healthcare and psychosocial support to students to improve their mental health and decrease the overall burden of depression.
Prospero registration number: CRD42023424301.
Keywords: depression & mood disorders; mental health; psychiatry.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of stress and associated factors among students in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2025 Feb 17;13:1518851. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1518851. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40034176 Free PMC article.
-
Common mental disorders and associated factors among Ethiopian prisoners: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jul 7;14:1214223. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1214223. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37484685 Free PMC article.
-
Burden and determinants of scabies in Ethiopian school age children: A systematic review and meta-analysis with public health implications.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 19;19(12):e0314882. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314882. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39700220 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of dysmenorrhea and associated factors among students in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Womens Health (Lond). 2022 Jan-Dec;18:17455057221079443. doi: 10.1177/17455057221079443. Womens Health (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35168425 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude and determinants of gender-based violence among female students in Ethiopian higher educational institutions: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Aug 22;15:1387032. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1387032. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39238935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marcus M, Yasamy MT, Ommeren MV, et al. . Depression: A global public health concern. 2012.
-
- Benjamin J, Verginal A. Kaplan & Sadok’s Synopsis of psychiatry behaviour science. Clinical Psychiatry 2007.
-
- Sadock BJ. Kaplan & Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer, 2015.
-
- Depression W. Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2017:24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous