The Minor Phytocannabinoid Delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritic Inflammation and Pain-Depressed Behaviors
- PMID: 38834355
- PMCID: PMC11493440
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.124.002189
The Minor Phytocannabinoid Delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritic Inflammation and Pain-Depressed Behaviors
Abstract
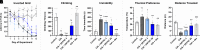
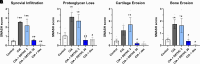
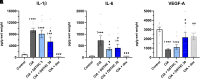
Patients with arthritis report using cannabis for pain management, and the major cannabinoid delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) has anti-inflammatory properties, yet the effects of minor cannabinoids on arthritis are largely unknown. The goal of the present study was to determine the antiarthritic potential of the minor cannabinoid delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC) using the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model. Adult male DBA/1J mice were immunized and boosted 21 days later with an emulsion of collagen and complete Freund's adjuvant. Beginning on the day of the booster, mice were administered twice-daily injections of Δ8-THC (3 or 30 mg/kg), the steroid dexamethasone (2 mg/kg), or vehicle for two weeks. Dorsal-ventral paw thickness and qualitative measures of arthritis were recorded daily, and latency to fall from an inverted grid was measured on alternating days, to determine arthritis severity and functional impairment. On the final day of testing, spontaneous wire-climbing behavior and temperature preference in a thermal gradient ring were measured to assess CIA-depressed behavior. The Δ8-THC treatment (30 mg/kg) reduced paw swelling and qualitative signs of arthritis. Δ8-THC also blocked CIA-depressed climbing and CIA-induced preference for a heated floor without producing locomotor effects but did not affect latency to fall from a wire grid. In alignment with the morphologic and behavioral assessments in vivo, histology revealed that Δ8-THC reduced synovial inflammation, proteoglycan loss and cartilage and bone erosion in the foot joints in a dose-dependent manner. Together, these findings suggest that Δ8-THC not only blocked morphologic changes but also prevented functional loss caused by collagen-induced arthritis. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Despite increasing use of cannabis products, the potential effects of minor cannabinoids are largely unknown. Here, the minor cannabinoid delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol blocked the development of experimentally induced arthritis by preventing both pathophysiological as well as functional effects of the disease model. These data support the development of novel cannabinoid treatments for inflammatory arthritis.
Copyright © 2024 by The Author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Monoacylglycerol Lipase Inhibition Using JZL184 Attenuates Paw Inflammation and Functional Deficits in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Arthritis.Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Jun;6(3):233-241. doi: 10.1089/can.2020.0177. Epub 2021 May 25. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021. PMID: 34042520 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-arthritic and anti-inflammatory effects of (-)-Epicatechin-3-O-β-d-allopyranoside, a constituent of Davallia formosana.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.192. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30599891
-
The antinociceptive effect of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the arthritic rat involves the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep 10;570(1-3):50-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.024. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17588560
-
Reversal of SR 141716A-induced head-twitch and ear-scratch responses in mice by delta 9-THC and other cannabinoids.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002 Jan-Feb;71(1-2):155-62. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(01)00647-5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002. PMID: 11812518
-
A Critical Review of the Role of the Cannabinoid Compounds Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) and their Combination in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment.Molecules. 2020 Oct 25;25(21):4930. doi: 10.3390/molecules25214930. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33113776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrahamov A, Abrahamov A, Mechoulam R (1995) An efficient new cannabinoid antiemetic in pediatric oncology. Life Sci 56:2097–2102. - PubMed
-
- Askling JBaecklund EGranath FGeborek PFored MBacklin CBertilsson LCöster LJacobsson LTLindblad S, et al. (2009) Anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and risk of malignant lymphomas: relative risks and time trends in the Swedish Biologics Register. Ann Rheum Dis 68:648–653 DOI: 10.1136/ARD.2007.085852. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baek SH, Kim YO, Kwag JS, Choi KE, Jung WY, Han DS (1998) Boron trifluoride etherate on silica-A modified Lewis acid reagent (VII). Antitumor activity of cannabigerol against human oral epitheloid carcinoma cells. Arch Pharm Res 21:353–356. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

