Enhanced analysis of tabular data through Multi-representation DeepInsight
- PMID: 38834670
- PMCID: PMC11724076
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63630-7
Enhanced analysis of tabular data through Multi-representation DeepInsight
Abstract
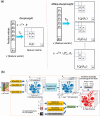
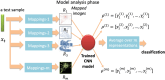
Tabular data analysis is a critical task in various domains, enabling us to uncover valuable insights from structured datasets. While traditional machine learning methods can be used for feature engineering and dimensionality reduction, they often struggle to capture the intricate relationships and dependencies within real-world datasets. In this paper, we present Multi-representation DeepInsight (MRep-DeepInsight), a novel extension of the DeepInsight method designed to enhance the analysis of tabular data. By generating multiple representations of samples using diverse feature extraction techniques, our approach is able to capture a broader range of features and reveal deeper insights. We demonstrate the effectiveness of MRep-DeepInsight on single-cell datasets, Alzheimer's data, and artificial data, showcasing an improved accuracy over the original DeepInsight approach and machine learning methods like random forest, XGBoost, LightGBM, FT-Transformer and L2-regularized logistic regression. Our results highlight the value of incorporating multiple representations for robust and accurate tabular data analysis. By leveraging the power of diverse representations, MRep-DeepInsight offers a promising new avenue for advancing decision-making and scientific discovery across a wide range of fields.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tabular deep learning: a comparative study applied to multi-task genome-wide prediction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Oct 4;25(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05940-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39367318 Free PMC article.
-
DeepInsight-3D architecture for anti-cancer drug response prediction with deep-learning on multi-omics.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 11;13(1):2483. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29644-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36774402 Free PMC article.
-
GeneViT: Gene Vision Transformer with Improved DeepInsight for cancer classification.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Mar;155:106643. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106643. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36803792
-
Advances in AI and machine learning for predictive medicine.J Hum Genet. 2024 Oct;69(10):487-497. doi: 10.1038/s10038-024-01231-y. Epub 2024 Feb 29. J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38424184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate predictions on small data with a tabular foundation model.Nature. 2025 Jan;637(8045):319-326. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08328-6. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39780007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma, A. & Paliwal, K. K. Linear discriminant analysis for the small sample size problem: an overview. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern.6, 443–454 (2015).
-
- Fukushima, K. Neocognitron. Scholarpedia2(1), 1717 (2007).
-
- Ho, T. K. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition 278–282 (1995).
-
- Duda, R. O. & Hart, P. E. Pattern classification and scene analysis. (Wiley, 1973).
-
- Bishop, C. M. Pattern recognition and machine learning. (Springer, 2006).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

