Suppressing mitochondrial inner membrane protein (IMMT) inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells through mitochondrial remodeling and metabolic regulation
- PMID: 38834715
- PMCID: PMC11150385
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63427-8
Suppressing mitochondrial inner membrane protein (IMMT) inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells through mitochondrial remodeling and metabolic regulation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Suppressing mitochondrial inner membrane protein (IMMT) inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells through mitochondrial remodeling and metabolic regulation.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74030-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455609 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
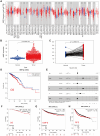
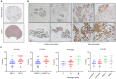
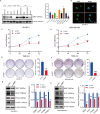
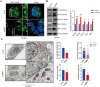
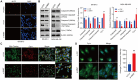
Metabolic reprogramming is widely recognized as a hallmark of malignant tumors, and the targeting of metabolism has emerged as an appealing approach for cancer treatment. Mitochondria, as pivotal organelles, play a crucial role in the metabolic regulation of tumor cells, and their morphological and functional alterations are intricately linked to the biological characteristics of tumors. As a key regulatory subunit of mitochondria, mitochondrial inner membrane protein (IMMT), plays a vital role in degenerative diseases, but its role in tumor is almost unknown. The objective of this research was to investigate the roles that IMMT play in the development and progression of breast cancer (BC), as well as to elucidate the underlying biological mechanisms that drive these effects. In this study, it was confirmed that the expression of IMMT in BC tissues was significantly higher than that in normal tissues. The analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database revealed that IMMT can serve as an independent prognostic factor for BC patients. Additionally, verification in clinical specimens of BC demonstrated a positive association between high IMMT expression and larger tumor size (> 2 cm), Ki-67 expression (> 15%), and HER-2 status. Furthermore, in vitro experiments have substantiated that the suppression of IMMT expression resulted in a reduction in cell proliferation and alterations in mitochondrial cristae, concomitant with the liberation of cytochrome c, but it did not elicit mitochondrial apoptosis. Through Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) analysis, we have predicted the associated metabolic genes and discovered that IMMT potentially modulates the advancement of BC through its interaction with 16 metabolic-related genes, and the changes in glycolysis related pathways have been validated in BC cell lines after IMMT inhibition. Consequently, this investigation furnishes compelling evidence supporting the classification of IMMT as prognostic marker in BC, and underscoring its prospective utility as a novel target for metabolic therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Metabolic reprogramming; Mitochondria remodeling; Mitochondrial inner membrane protein (IMMT); Prognostic marker.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-omics and experimental analysis unveil theragnostic value and immunological roles of inner membrane mitochondrial protein (IMMT) in breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2023 Mar 10;21(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04035-4. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36899366 Free PMC article.
-
Supervised Learning and Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Clinical Significance of Inner Membrane Mitochondrial Protein (IMMT) in Prognostic Prediction, Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Precision Medicine for Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8807. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108807. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240154 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of IMMT expression in surgically-resected lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Nov;10(11):2142-2151. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13200. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31583841 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and their role in breast cancer metabolism (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Jan;66(1):7. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5713. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39635852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid metabolic reprograming: the unsung hero in breast cancer progression and tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2025 Mar 3;24(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02258-1. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40025508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the pathogenesis of mitochondria in breast cancer and progress of targeting mitochondria for breast cancer treatment.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 15;23(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06077-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39815317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E. & Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin.72(1), 7–33 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

