PARP14 and PARP9/DTX3L regulate interferon-induced ADP-ribosylation
- PMID: 38834853
- PMCID: PMC11251020
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00126-0
PARP14 and PARP9/DTX3L regulate interferon-induced ADP-ribosylation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: PARP14 and PARP9/DTX3L regulate interferon-induced ADP-ribosylation.EMBO J. 2024 Nov;43(21):5327. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00247-6. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39322761 Free PMC article.
Abstract
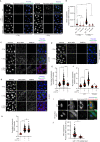
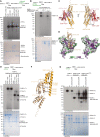
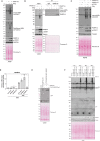
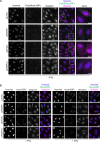
PARP-catalysed ADP-ribosylation (ADPr) is important in regulating various cellular pathways. Until recently, PARP-dependent mono-ADP-ribosylation has been poorly understood due to the lack of sensitive detection methods. Here, we utilised an improved antibody to detect mono-ADP-ribosylation. We visualised endogenous interferon (IFN)-induced ADP-ribosylation and show that PARP14 is a major enzyme responsible for this modification. Fittingly, this signalling is reversed by the macrodomain from SARS-CoV-2 (Mac1), providing a possible mechanism by which Mac1 counteracts the activity of antiviral PARPs. Our data also elucidate a major role of PARP9 and its binding partner, the E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX3L, in regulating PARP14 activity through protein-protein interactions and by the hydrolytic activity of PARP9 macrodomain 1. Finally, we also present the first visualisation of ADPr-dependent ubiquitylation in the IFN response. These approaches should further advance our understanding of IFN-induced ADPr and ubiquitin signalling processes and could shed light on how different pathogens avoid such defence pathways.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylation; Immune Response; Interferon Response; SARS-CoV2; Ubiquitin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MN is an employee and shareholder of Ribon Therapeutics. EP is an employee of Vertex Pharmaceuticals and may own stock or stock options in that company. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Aguiar RCT, Takeyama K, He C, Kreinbrink K, Shipp MA (2005) B-aggressive lymphoma family proteins have unique domains that modulate transcription and exhibit poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity. J Biol Chem 280:33756–33765 - PubMed
-
- Ahel I, Ahel D, Matsusaka T, Clark AJ, Pines J, Boulton SJ, West SC (2008) Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature 451:81–85 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CD53/Ligue Contre le Cancer (French League Against Cancer)
- ANR-22-CE12-0039/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR)
- 223107/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/R007195/1/UKRI | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- ARCPJA2022060005190/Fondation ARC pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

