XIST dampens X chromosome activity in a SPEN-dependent manner during early human development
- PMID: 38834912
- PMCID: PMC11479943
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01325-3
XIST dampens X chromosome activity in a SPEN-dependent manner during early human development
Abstract
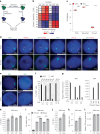
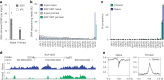
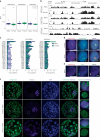
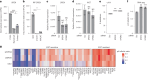
XIST (X-inactive specific transcript) long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is responsible for X chromosome inactivation (XCI) in placental mammals, yet it accumulates on both X chromosomes in human female preimplantation embryos without triggering X chromosome silencing. The XACT (X-active coating transcript) lncRNA coaccumulates with XIST on active X chromosomes and may antagonize XIST function. Here, we used human embryonic stem cells in a naive state of pluripotency to assess the function of XIST and XACT in shaping the X chromosome chromatin and transcriptional landscapes during preimplantation development. We show that XIST triggers the deposition of polycomb-mediated repressive histone modifications and dampens the transcription of most X-linked genes in a SPEN-dependent manner, while XACT deficiency does not significantly affect XIST activity or X-linked gene expression. Our study demonstrates that XIST is functional before XCI, confirms the existence of a transient process of X chromosome dosage compensation and reveals that XCI and dampening rely on the same set of factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



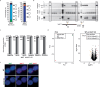


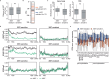
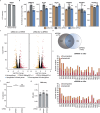
References
-
- Avner, P. & Heard, E. X-chromosome inactivation: counting, choice and initiation. Nat. Rev. Genet.2, 59–67 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Plath, K., Mlynarczyk-Evans, S., Nusinow, D. A. & Panning, B. XIST RNA and the mechanism of X chromosome inactivation. Annu. Rev. Genet.36, 233–278 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Hadjantonakis, A.-K., Cox, L. L., Tam, P. P. L. & Nagy, A. An X-linked GFP transgene reveals unexpected paternal X-chromosome activity in trophoblastic giant cells of the mouse placenta. Genesis29, 133–140 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Sugimoto, M., Tan, S. S. & Takagi, N. X chromosome inactivation revealed by the X-linked lacZ transgene activity in periimplantation mouse embryos. Int. J. Dev. Biol.44, 177–182 (2000). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

