miR-486-5p predicted adverse outcomes of SCAP and regulated K. pneumonia infection via FOXO1
- PMID: 38834979
- PMCID: PMC11149205
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-024-00624-0
miR-486-5p predicted adverse outcomes of SCAP and regulated K. pneumonia infection via FOXO1
Abstract
Purpose: Severe community-acquired pneumonia (SCAP) is a common respiratory system disease with rapid development and high mortality. Exploring effective biomarkers for early detection and development prediction of SCAP is of urgent need. The function of miR-486-5p in SCAP diagnosis and prognosis was evaluated to identify a promising biomarker for SCAP.
Patients and methods: The serum miR-486-5p in 83 patients with SCAP, 52 healthy individuals, and 68 patients with mild CAP (MCAP) patients were analyzed by PCR. ROC analysis estimated miR-486-5p in screening SCAP, and the Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses evaluated the predictive value of miR-486-5p. The risk factors for MCAP patients developing SCAP were assessed by logistic analysis. The alveolar epithelial cell was treated with Klebsiella pneumonia to mimic the occurrence of SCAP. The targeting mechanism underlying miR-486-5p was evaluated by luciferase reporter assay.
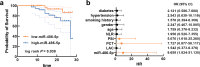
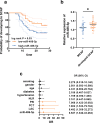
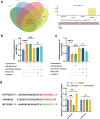
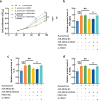
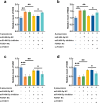
Results: Upregulated serum miR-486-5p screened SCAP from healthy individuals and MCAP patients with high sensitivity and specificity. Increasing serum miR-486-5p predicted the poor outcomes of SCAP and served as a risk factor for MCAP developing into SCAP. K. pneumonia induced suppressed proliferation, significant inflammation and oxidative stress in alveolar epithelial cells, and silencing miR-486-5p attenuated it. miR-486-5p negatively regulated FOXO1, and the knockdown of FOXO1 reversed the effect of miR-486-5p in K. pneumonia-treated alveolar epithelial cells.
Conclusion: miR-486-5p acted as a biomarker for the screening and monitoring of SCAP and predicting the malignancy of MCAP. Silencing miR-486-5p alleviated inflammation and oxidative stress induced by K. pneumonia via negatively modulating FOXO1.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Inflammatory response; Malignancy; Oxidative stress; Prognosis; Severity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-151a-5p predicts severity of diabetic retinopathy and protects from retinal cell injury by inactivating MAPK signaling via DKK3.Exp Eye Res. 2025 Feb;251:110212. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2024.110212. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Exp Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 39701171
-
Urine miR-340-5p Predicts the Adverse Prognosis of Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury and Regulates Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury by Targeting KDM4C.Nephron. 2025;149(4):197-206. doi: 10.1159/000541348. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Nephron. 2025. PMID: 39551047
-
Potential of miR-192-5p as a diagnostic marker for children with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure and its predictive value for prognosis.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2025;50(1):98-104. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2025.149249. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40620650 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of severe community-acquired pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2012 Jul 27;16(4):R141. doi: 10.1186/cc11447. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22839689 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in oral fluids (saliva and gingival crevicular fluid) as biomarkers in orthodontics: systematic review and integrated bioinformatic analysis.Prog Orthod. 2021 Oct 11;22(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40510-021-00377-1. Prog Orthod. 2021. PMID: 34632546 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LncRNA CYP1B1-AS1 as a clinical biomarker exacerbates sepsis inflammatory response via targeting miR- 18a- 5p.BMC Immunol. 2025 Apr 16;26(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12865-025-00712-9. BMC Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40234801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartoš H, Džupová O. Severe community-acquired pneumonia in intensive care. Epidemiologie, mikrobiologie, imunologie: casopis spolecnosti pro epidemiologii a mikrobiologii ceske lekarske spolecnosti. JE Purkyne. 2020;69(4):159–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

