Empathy in undergraduate medical students: a multi-center cross-sectional study in China
- PMID: 38834981
- PMCID: PMC11151548
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-023-05350-2
Empathy in undergraduate medical students: a multi-center cross-sectional study in China
Abstract
Background: Fostering empathy has been continuously emphasized in the global medical education. Empathy is crucial to enhance patient-physician relationships, and is associated with medical students' academic and clinical performance. However, empathy level of medical students in China and related influencing factors are not clear.
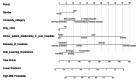
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study among medical students in 11 universities. We used the Jefferson Scale of Empathy Student-version of Chinese version to measure empathy level of medical students. Factors associated with empathy were identified by the univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Based on the variables identified above, the nomogram was established to predict high empathy probability of medical students. Receiver operating characteristic curve, calibration plot and decision curve analysis were used to evaluate the discrimination, calibration and educational utility of the model.
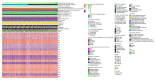
Results: We received 10,901 samples, but a total of 10,576 samples could be used for further analysis (effective response rate of 97.02%). The mean empathy score of undergraduate medical students was 67.38 (standard deviation = 9.39). Six variables including gender, university category, only child or not, self-perception doctor-patient relationship in hospitals, interest of medicine, Kolb learning style showed statistical significance with empathy of medical students (P < 0.05). Then, the nomogram was established based on six variables. The validation suggested the nomogram model was well calibrated and had good utility in education, as well as area under the curve of model prediction was 0.65.
Conclusions: We identify factors influencing empathy of undergraduate medical students. Moreover, increasing manifest and hidden curriculums on cultivating empathy of medical students may be needed among medical universities or schools in China.
Keywords: Empathy; Influencing factors; Medical students; Nomogram.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multi-institutional and cross-sectional study on empathy in Chinese medical students: differences by student cadre or not, future career preference, and father's education status.BMC Med Educ. 2020 Jan 28;20(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-1935-x. BMC Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 31992284 Free PMC article.
-
Empathy variation of undergraduate medical students after early clinical contact: a cross-sectional study in China.BMJ Open. 2020 Jul 19;10(7):e035690. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035690. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32690511 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical empathy in medical students in India measured using the Jefferson Scale of Empathy-Student Version.J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017 Dec 27;14:33. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2017.14.33. eCollection 2017. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017. PMID: 29278905 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-center cross-sectional study on identification of influencing factors of medical students' emotional engagement in China.BMC Med Educ. 2023 Nov 7;23(1):838. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04504-w. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 37936085 Free PMC article.
-
The level and determinants of empathy among medical students from Arabic speaking countries: A systematic review.GMS J Med Educ. 2024 Apr 15;41(2):Doc15. doi: 10.3205/zma001670. eCollection 2024. GMS J Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38779697 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of grade point average on medical students' perception of the learning environment: a multicenter cross-sectional study across 12 Chinese medical schools.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Mar 27;25(1):448. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-06977-3. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40148831 Free PMC article.
-
Top-tier ranking university bring worse perception of medical learning environment to students: a cross-sectional study across 12 universities.Med Educ Online. 2025 Dec;30(1):2542806. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2025.2542806. Epub 2025 Aug 7. Med Educ Online. 2025. PMID: 40772885 Free PMC article.
-
Learning environment as a predictor for medical students' empathy: a multicenter cross-sectional study from 12 medical schools in China.BMC Psychol. 2025 Jan 3;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-02174-x. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39754270 Free PMC article.
-
Empathy, Moral Sensitivity, and Prosocial Behavior Among Medical Undergraduates in a South Indian Tertiary Care Teaching Institute: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2024 Sep 28;16(9):e70392. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70392. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39469398 Free PMC article.
-
The Chinese-Adapted Jefferson Scale of Empathy - Medical Student Version for Assessing the Level of Empathy in Medical Students: A Study of the Reliability and Validity.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2025 May 31;16:943-952. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S514231. eCollection 2025. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2025. PMID: 40470263 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

