Comparison of hypotension incidence between remimazolam and propofol in patients with hypertension undergoing neurosurgery: prospective, randomized, single-blind trial
- PMID: 38834996
- PMCID: PMC11149299
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-024-02578-7
Comparison of hypotension incidence between remimazolam and propofol in patients with hypertension undergoing neurosurgery: prospective, randomized, single-blind trial
Abstract
Background: Remimazolam, a newer benzodiazepine that targets the GABAA receptor, is thought to allow more stable blood pressure management during anesthesia induction. In contrast, propofol is associated with vasodilatory effects and an increased risk of hypotension, particularly in patients with comorbidities. This study aimed to identify medications that can maintain stable vital signs throughout the induction phase.
Methods: We conducted a single-center, two-group, randomized controlled trial to investigate and compare the incidence of hypotension between remimazolam- and propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA). We selected patients aged between 19 and 75 years scheduled for neurosurgery under general anesthesia, who were classified as American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status I-III and had a history of hypertension.
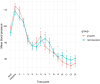
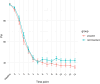
Results: We included 94 patients in the final analysis. The incidence of hypotension was higher in the propofol group (91.3%) than in the remimazolam group (85.4%; P = 0.057). There was no significant difference in the incidence of hypotension among the various antihypertensive medications despite the majority of patients being on multiple medications. In comparison with the propofol group, the remimazolam group demonstrated a higher heart rate immediately after intubation.
Conclusions: Our study indicated that the hypotension incidence of remimazolam-based TIVA was comparable to that of propofol-based TIVA throughout the induction phase of EEG-guided anesthesia. Both remimazolam and propofol may be equally suitable for general anesthesia in patients undergoing neurosurgery.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT05164146).
Keywords: Anesthetic induction; Drug therapy; Hypertension; Propofol; Remimazolam.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing the safety and efficacy of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia versus volatile agent-based anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025 Feb;78(1):48-60. doi: 10.4097/kja.24444. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39663669 Free PMC article.
-
Hypotension after general anaesthesia induction using remimazolam or propofol in geriatric patients undergoing sevoflurane anaesthesia with remifentanil: a single-centre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial.Br J Anaesth. 2024 Jul;133(1):24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2024.04.013. Epub 2024 May 22. Br J Anaesth. 2024. PMID: 38777646 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of remimazolam-based and propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia on hemodynamics during anesthesia induction in patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a randomized controlled trial.J Anesth. 2024 Jun;38(3):330-338. doi: 10.1007/s00540-024-03311-x. Epub 2024 Feb 12. J Anesth. 2024. PMID: 38347233 Clinical Trial.
-
Post-induction hypotension with remimazolam versus propofol in patients routinely administered angiotensin axis blockades: a randomized control trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Jun 22;23(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02188-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37349690 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Remimazolam vs. propofol for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of emergence agitation risk in surgical populations.J Clin Anesth. 2025 Apr;103:111815. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2025.111815. Epub 2025 Mar 22. J Clin Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40120546
Cited by
-
Comparing the safety and efficacy of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia versus volatile agent-based anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025 Feb;78(1):48-60. doi: 10.4097/kja.24444. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39663669 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of remimazolam on postoperative delirium and cognitive function in adults undergoing general anesthesia or procedural sedation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025 Apr;78(2):118-128. doi: 10.4097/kja.24493. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39748753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoon U, Setren A, Chen A, Nguyen T, Torjman M, Kennedy T. Continuation of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on the day of surgery is not associated with increased risk of hypotension upon induction of general anesthesia in elective noncardiac surgeries. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2021;35:508–513. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2020.01.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Malinowska-Zaprzałka M, Wojewódzka M, Dryl D, Grabowska SZ, Chabielska E. Hemodynamic effect of propofol in enalapril-treated hypertensive patients during induction of general anesthesia. Pharmacol Rep. 2005;57:675–8. - PubMed
-
- Oczenski W, Krenn H, Dahaba AA, Binder M, El-Schahawi-Kienzl I, Jellinek H, et al. Hemodynamic and Catecholamine stress responses to insertion of the combitube, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal intubation. Anesth Analg. 1999;88:1389–1394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

