Serum Lipoprotein(a) Levels as a Predictor of Aortic Stiffness in Patients on Long-Term Peritoneal Dialysis
- PMID: 38835156
- PMCID: PMC11163936
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944348
Serum Lipoprotein(a) Levels as a Predictor of Aortic Stiffness in Patients on Long-Term Peritoneal Dialysis
Abstract
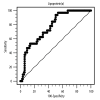
BACKGROUND Lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] is associated with atherosclerosis and cardiovascular mortality in patients with kidney failure. Aortic stiffness (AS), measured primarily by carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV), reflects vascular aging and precedes end-organ failure. This study aimed to evaluate the association between serum Lp(a) levels and cfPWV in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD). MATERIAL AND METHODS In this cross-sectional study, which included 148 patients with long-term PD for end-stage kidney failure, cfPWV was measured using a cuff-based method. AS was defined as a cfPWV exceeding 10 m/s, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine serum Lp(a) levels. Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were performed to identify the clinical correlates of AS. RESULTS There were 32 (21.6%) patients diagnosed with AS. Based on the multivariate logistic regression analysis, the odds ratio for AS was 1.007 (95% confidence interval, 1.003-1.011; P=0.001) for every 1 mg/L increase in Lp(a) levels. Multivariate linear regression analysis showed that Lp(a) (P<0.001), age (P=0.003), waist circumference (P=0.008), systolic blood pressure (P=0.010), and diabetes mellitus (P<0.001) were positively associated with cfPWV. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for Lp(a) in differentiating AS from non-AS was 0.770 (95% confidence interval, 0.694-0.835; P<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS Serum Lp(a) level was independently associated with cfPWV and AS in patients with PD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum osteoprotegerin is an independent marker of central arterial stiffness as assessed using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity in hemodialysis patients: a cross sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2019 May 23;20(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1374-2. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31122190 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Arterial Stiffness in Chronic Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Dec 3;16(12):523. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120523. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728781 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Endocan Is a Risk Factor for Aortic Stiffness in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 14;60(6):984. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060984. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929601 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Association of Serum Galectin-3 with the Development of Aortic Stiffness of Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis.J Clin Med. 2023 May 17;12(10):3519. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103519. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240626 Free PMC article.
-
Serum leptin levels are positively associated with aortic stiffness in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3-5.Adipocyte. 2020 Dec;9(1):206-211. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2020.1764799. Adipocyte. 2020. PMID: 32403968 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Klotho enhances stability of chronic kidney disease atherosclerotic plaques by inhibiting GRK2/PLC-β-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in macrophages via modulation of the ROS/SHP1 pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32091. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83596-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738381 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Adverse Outcomes in Heart Failure.J Card Fail. 2025 Apr 4:S1071-9164(25)00160-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2025.03.016. Online ahead of print. J Card Fail. 2025. PMID: 40189094
-
Association Between Lipoprotein(a) and Arterial Stiffness in Young Adults with Familial Hypercholesterolemia.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 27;14(5):1611. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051611. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Biesen W, Verbeke F, Vanholder R. Cardiovascular disease in haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: Arguments pro peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22(1):53–58. - PubMed
-
- Lee CC, Hsu CC, Lin MH, et al. Hospitalization in patients with dialysis in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based observational study. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022;121(Suppl 1):S39–S46. - PubMed
-
- Krediet RT, Balafa O. Cardiovascular risk in the peritoneal dialysis patient. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(8):451–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous