The m6A reader ECT8 is an abiotic stress sensor that accelerates mRNA decay in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 38835286
- PMCID: PMC11289641
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koae149
The m6A reader ECT8 is an abiotic stress sensor that accelerates mRNA decay in Arabidopsis
Abstract
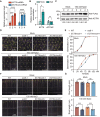
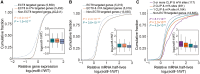
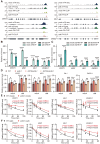
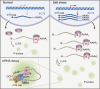
N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant mRNA modification and plays diverse roles in eukaryotes, including plants. It regulates various processes, including plant growth, development, and responses to external or internal stress responses. However, the mechanisms underlying how m6A is related to environmental stresses in both mammals and plants remain elusive. Here, we identified EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED C-TERMINAL REGION 8 (ECT8) as an m6A reader protein and showed that its m6A-binding capability is required for salt stress responses in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). ECT8 accelerates the degradation of its target transcripts through direct interaction with the decapping protein DECAPPING 5 within processing bodies. We observed a significant increase in the ECT8 expression level under various environmental stresses. Using salt stress as a representative stressor, we found that the transcript and protein levels of ECT8 rise in response to salt stress. The increased abundance of ECT8 protein results in the enhanced binding capability to m6A-modified mRNAs, thereby accelerating their degradation, especially those of negative regulators of salt stress responses. Our results demonstrated that ECT8 acts as an abiotic stress sensor, facilitating mRNA decay, which is vital for maintaining transcriptome homeostasis and enhancing stress tolerance in plants. Our findings not only advance the understanding of epitranscriptomic gene regulation but also offer potential applications for breeding more resilient crops in the face of rapidly changing environmental conditions.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adding salt to the mix: The m6A reader ECT8 is a stress sensor, expediting mRNA decay in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2024 Jul 31;36(8):2757-2758. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae156. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38788742 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
ECT8, an mRNA m6A reader, enhances salt stress tolerance by modulating mRNA stability in Arabidopsis.Physiol Plant. 2025 Jan-Feb;177(1):e70135. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70135. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 39968864
-
N6-methyladenosine-mediated feedback regulation of abscisic acid perception via phase-separated ECT8 condensates in Arabidopsis.Nat Plants. 2024 Mar;10(3):469-482. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01638-7. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Nat Plants. 2024. PMID: 38448725
-
Epitranscriptomic mRNA modifications governing plant stress responses: underlying mechanism and potential application.Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Dec;20(12):2245-2257. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13913. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36002976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Budding yeast as an ideal model for elucidating the role of N6-methyladenosine in regulating gene expression.Yeast. 2024 Apr;41(4):148-157. doi: 10.1002/yea.3925. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Yeast. 2024. PMID: 38238962 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection, distribution, and functions of RNA N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) in plant development and environmental signal responses.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jul 16;15:1429011. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1429011. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39081522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adding salt to the mix: The m6A reader ECT8 is a stress sensor, expediting mRNA decay in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2024 Jul 31;36(8):2757-2758. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae156. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38788742 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Regulatory Roles of RNA-Binding Proteins in Plant Salt Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 7;14(9):1402. doi: 10.3390/plants14091402. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Members in the YT521-B Homology Domain-Containing RNA Binding Protein Family in Ginkgo biloba.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 23;13(24):3589. doi: 10.3390/plants13243589. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771287 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Identification of m6A Writers, Erasers and Readers and Their Expression Profiles under Various Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Pinus massoniana Lamb.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 22;25(14):7987. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147987. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat SS, Bielewicz D, Gulanicz T, Bodi Z, Yu X, Anderson SJ, Szewc L, Bajczyk M, Dolata J, Grzelak N, et al. . mRNA adenosine methylase (MTA) deposits m6A on pri-miRNAs to modulate miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020:117(35):21785–21795. 10.1073/pnas.2003733117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

