Mechanisms underlying reversed TRAIL sensitivity in acquired bortezomib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 38835345
- PMCID: PMC11149110
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2024.14
Mechanisms underlying reversed TRAIL sensitivity in acquired bortezomib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
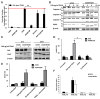
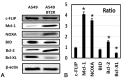
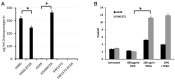
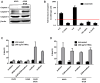
Aim: The therapeutic targeting of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptors in cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), is a widely studied approach for tumor selective apoptotic cell death therapy. However, apoptosis resistance is often encountered. The main aim of this study was to investigate the apoptotic mechanism underlying TRAIL sensitivity in three bortezomib (BTZ)-resistant NSCLC variants, combining induction of both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Methods: Sensitivity to TRAIL in BTZ-resistant variants was determined using a tetrazolium (MTT) and a clonogenic assay. A RT-qPCR profiling mRNA array was used to determine apoptosis pathway-specific gene expression. The expression of these proteins was determined through ELISA assays and western Blotting, while apoptosis (sub-G1) and cytokine expression were determined using flow cytometry. Apoptotic genes were silenced by specific siRNAs. Lipid rafts were isolated with fractional ultracentrifugation. Results: A549BTZR (BTZ-resistant) cells were sensitive to TRAIL in contrast to parental A549 cells, which are resistant to TRAIL. TRAIL-sensitive H460 cells remained equally sensitive for TRAIL as H460BTZR. In A549BTZR cells, we identified an increased mRNA expression of TNFRSF11B [osteoprotegerin (OPG)] and caspase-1, -4 and -5 mRNAs involved in cytokine activation and immunogenic cell death. Although the OPG, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-8 (IL-8) protein levels were markedly enhanced (122-, 103-, and 11-fold, respectively) in the A549BTZR cells, this was not sufficient to trigger TRAIL-induced apoptosis in the parental A549 cells. Regarding the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, the A549BTZR cells showed TRAIL-R1-dependent TRAIL sensitivity. The shift of TRAIL-R1 from non-lipid into lipid rafts enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, a strong increase in the mRNA and protein levels of the anti-apoptotic myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (Mcl-1) and B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) was found, whereas the B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) expression was reduced. However, the stable overexpression of Bcl-xL in the A549BTZR cells did not reverse the TRAIL sensitivity in the A549BTZR cells, but silencing of the BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist (BID) protein demonstrated the importance of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, regardless of Bcl-xL. Conclusion: In summary, increased sensitivity to TRAIL-R1 seems predominantly related to the relocalization into lipid rafts and increased extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways.
Keywords: Bcl-2 family; TRAIL; bortezomib; cytokines; lipid rafts; resistance; sensitization.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Peters GJ is an Editorial Board Member of the journal Cancer Drug Resistance, while the other authors have declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanisms underlying synergism between circularized tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand and bortezomib in bortezomib-sensitive or -resistant myeloma cells.Hematol Oncol. 2022 Dec;40(5):999-1008. doi: 10.1002/hon.3045. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35789025 Free PMC article.
-
Chalepin: A Compound from Ruta angustifolia L. Pers Exhibits Cell Cycle Arrest at S phase, Suppresses Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway, Signal Transducer and Activation of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Phosphorylation and Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Carcinoma (A549).Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Oct;13(Suppl 3):S489-S498. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_13_17. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 29142404 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL therapy in non-small cell lung cancer cells: sensitization to death receptor-mediated apoptosis by proteasome inhibitor bortezomib.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jul;6(7):2103-12. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0167. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17620439
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
-
uHTS for the identification of compounds that potentiate TRAIL-induced apoptosis of cancer cells.2009 May 18 [updated 2010 Sep 2]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2009 May 18 [updated 2010 Sep 2]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 21433372 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Niemira M, Collin F, Szalkowska A, et al. Molecular signature of subtypes of non-small-cell lung cancer by large-scale transcriptional profiling: identification of key modules and genes by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) Cancers. 2019;12:37. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
