Lactate and lactylation in macrophage metabolic reprogramming: current progress and outstanding issues
- PMID: 38835758
- PMCID: PMC11148263
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395786
Lactate and lactylation in macrophage metabolic reprogramming: current progress and outstanding issues
Abstract
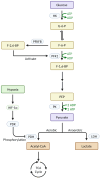
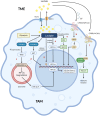
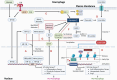
It is commonly known that different macrophage phenotypes play specific roles in different pathophysiological processes. In recent years, many studies have linked the phenotypes of macrophages to their characteristics in different metabolic pathways, suggesting that macrophages can perform different functions through metabolic reprogramming. It is now gradually recognized that lactate, previously overlooked as a byproduct of glycolytic metabolism, acts as a signaling molecule in regulating multiple biological processes, including immunological responses and metabolism. Recently, lactate has been found to mediate epigenetic changes in macrophages through a newfound lactylation modification, thereby regulating their phenotypic transformation. This novel finding highlights the significant role of lactate metabolism in macrophage function. In this review, we summarize the features of relevant metabolic reprogramming in macrophages and the role of lactate metabolism therein. We also review the progress of research on the regulation of macrophage metabolic reprogramming by lactylation through epigenetic mechanisms.
Keywords: Post-translational modification (PTM); lactate; lactylation; macrophage; metabolic reprogramming.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Liu, Li and Geng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

