Cynaroside ameliorates methotrexate-induced enteritis in rats through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 38835771
- PMCID: PMC11148340
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1405084
Cynaroside ameliorates methotrexate-induced enteritis in rats through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
Introduction: Cynaroside exhibits various biological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antitumor, and cardioprotective effects. However, its involvement in methotrexate (MTX)-induced intestinal inflammation remains inadequately understood. Thus, we investigated the impact of cynaroside on MTX-induced intestinal inflammation and its potential mechanisms.
Methods: To assess the protective potential of cynaroside against intestinal inflammation, Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to a regimen of 7 mg/kg MTX for 3 days, followed by treatment with cynaroside at varying doses (10, 20, or 40 mg/kg). Histopathological evaluations were conducted alongside measurements of inflammatory mediators to elucidate the involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in alleviating intestinal inflammation.
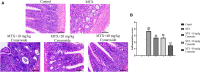
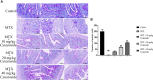
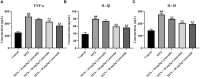
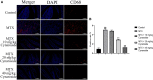
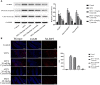
Results: Administration of 7 mg/kg MTX resulted in decreased daily food intake, increased weight loss, and elevated disease activity index in rats. Conversely, treatment with cynaroside at 20 or 40 mg/kg ameliorated the reductions in body weight and daily food intake and suppressed the MTX-induced elevation in the disease activity index. Notably, cynaroside administration at 20 or 40 mg/kg attenuated inflammatory cell infiltration, augmented goblet cell numbers and lowered serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-18, as well as the CD68-positive cell rate in the intestines of MTX-induced rats. Furthermore, cynaroside downregulated the expression levels of NLRP3, cleaved caspase 1, and cleaved IL-1β in MTX-induced rats.
Discussion: Collectively, our findings indicated that cymaroside alleviates intestinal inflammatory injury by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in MTX-induced rats.
Keywords: NLRP3; cleaved IL-1β; cleaved caspase 1; cynaroside; intestinal inflammation; methotrexate.
Copyright © 2024 Lang, Wen, Zhang, Liang, Chen, Zhang, Zhou, Ali, Hu, Zhang and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
Author WL, XL and MC were employed by the company Shaanxi Qinling Industrial Technology Research Institute of Special Biological Resources Co. Ltd. Author DZ was employed by the company Shaanxi Panlong Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
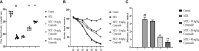
Similar articles
-
Aucubin alleviates methotrexate-induced enteritis in rats by inducing autophagy.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023 Nov;50(11):855-866. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13810. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37582493
-
Albiflorin ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in Methotrexate-induced enteritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108824. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108824. Epub 2022 May 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35561481
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Forsythiaside A alleviates methotrexate-induced intestinal mucositis in rats by modulating the NLRP3 signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Feb;103:108466. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108466. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34933162
-
Rosiglitazone ameliorates radiation-induced intestinal inflammation in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and TNF-α production.J Radiat Res. 2020 Nov 16;61(6):842-850. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa062. J Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32876675 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cynaroside ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 20;15:1496068. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1496068. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39902073 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

