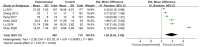Factors contributing to sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38835794
- PMCID: PMC11148246
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1379019
Factors contributing to sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This study aims to systematically assess the risk factors, the overall strength of association, and evidence quality related to sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase for cohort or case-control studies published up to August 2023 on risk factors associated with sepsis-related encephalopathy. The selected studies were screened, data were extracted, and the quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The certainty of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE criteria.
Results: A total of 13 studies involving 1,906 participants were included in the analysis. Among these studies, 12 were of high quality, and one was of moderate quality. Our meta-analysis identified six risk factors significantly associated with Serious Adverse Events (SAE). These included APACHE II, SOFA, age, tau protein, and IL-6, which were found to be risk factors with significant effects (standard mean difference SMD: 1.24-2.30), and albumin, which was a risk factor with moderate effects (SMD: -0.55). However, the certainty of evidence for the risk factors identified in this meta-analysis ranged from low to medium.
Conclusion: This systematic review and meta-analysis identified several risk factors with moderate to significant effects. APACHE II, SOFA, age, tau protein, IL-6, and albumin were associated with sepsis-related encephalopathy and were supported by medium- to high-quality evidence. These findings provide healthcare professionals with an evidence-based foundation for managing and treating hospitalized adult patients with sepsis-related encephalopathy.
Keywords: delirium; encephalopathy; meta-analysis; risk factors; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Guo, Jia, Duo, Shen and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of evaluating neuron specific enolase as a serum biomarker for sepsis-associated encephalopathy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Apr 20;131:111857. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111857. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38489973
-
Characterization of Sepsis and Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy.J Intensive Care Med. 2019 Nov-Dec;34(11-12):938-945. doi: 10.1177/0885066617719750. Epub 2017 Jul 18. J Intensive Care Med. 2019. PMID: 28718340
-
Mindfulness-based stress reduction for women diagnosed with breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 27;3(3):CD011518. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011518.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30916356 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial interventions for preventing and treating depression in dialysis patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 2;12(12):CD004542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004542.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31789430 Free PMC article.
-
[Construction and analysis of early warning and prediction model for risk factors of sepsis-associated encephalopathy].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Feb;36(2):124-130. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231008-00847. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38442925 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Role of Ultrasonographic Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter in Prediction of Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy: Prospective Observational Study.Neurocrit Care. 2025 Aug;43(1):308-317. doi: 10.1007/s12028-024-02187-9. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Neurocrit Care. 2025. PMID: 39815108 Free PMC article.
-
Acute hyperglycemia exacerbates neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in sepsis-associated encephalopathy by mediating the ChREBP/HIF-1α pathway.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Nov 14;29(1):546. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02129-3. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39538358 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of sedation and analgesia scores on prognosis in critically ill sepsis patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a retrospective analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1622964. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1622964. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40635709 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic models for sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1645397. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1645397. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40823290 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological and clinical predictors of sepsis-associated encephalopathy in bloodstream infections: a retrospective cohort study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 7;15:1548370. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1548370. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40125514 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources