Construction of competing endogenous RNA networks in systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated analysis
- PMID: 38835801
- PMCID: PMC11149421
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1383186
Construction of competing endogenous RNA networks in systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated analysis
Abstract
Objective: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a disease characterised by immune inflammation and damage to multiple organs. Recent investigations have linked competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) to lupus. However, the exact mechanism through which the ceRNAs network affects SLE is still unclear. This study aims to investigate the regulatory functions of the ceRNAs network, which are important pathways that control the pathophysiological processes of SLE.
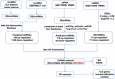
Methods: CircRNA microarray for our tested assays were derived from bone marrow samples from three healthy individuals and three SLE patients in our hospital. The other sequencing data of circRNA, miRNA and mRNA were obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. Using the limma package of R program, the differential expression of mRNA and miRNA in the GEO database was discovered. Then predicted miRNA-mRNA and circRNA-miRNA were established using miRMap, miRanda, miRDB, TargetScan, and miTarBase. CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network was constructed using Cytoscape, and hub genes were screened using a protein-protein interaction network. Immune infiltration analysis of the hub gene was also performed by CIBERSORT and GSEA.
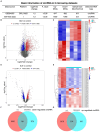
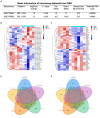
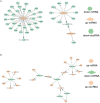
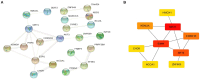
Results: 230 overlapped circRNAs, 86 DEmiRNAs and 2083 DEmRNAs were identified in SLE patients as compared to healthy controls. We constructed a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNAs network contained 11 overlapped circRNAs, 9 miRNAs and 51 mRNAs. ESR1 and SIRT1 were the most frequently associated protein-protein interactions in the PPI network. KEGG analysis showed that DEGs was enriched in FoxO signaling pathway as well as lipids and atherosclerosis. We constructed a novel circRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network (HSA circ 0000345- HSA miR-22-3-P-ESR1/SIRT1) that may have a major impact on SLE.
Conclusion: Through this bioinformatics and integrated analysis, we suggest a regulatory role for ceRNA network in the pathogenesis and treatment of SLE.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; competing endogenous RNAs; differentially expressed genes; enrichment analysis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2024 He, Dai, Liu, Lin, Gao, Chen and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

