A one-step low-cost molecular test for SARS-CoV-2 detection suitable for community testing using minimally processed saliva
- PMID: 38835855
- PMCID: PMC11147803
- DOI: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae035
A one-step low-cost molecular test for SARS-CoV-2 detection suitable for community testing using minimally processed saliva
Abstract
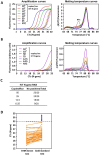
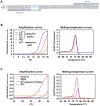
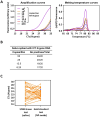
The gold standard for coronavirus disease 2019 diagnostic testing relies on RNA extraction from naso/oropharyngeal swab followed by amplification through reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with fluorogenic probes. While the test is extremely sensitive and specific, its high cost and the potential discomfort associated with specimen collection made it suboptimal for public health screening purposes. In this study, we developed an equally reliable, but cheaper and less invasive alternative test based on a one-step RT-PCR with the DNA-intercalating dye SYBR Green, which enables the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) directly from saliva samples or RNA isolated from nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs. Importantly, we found that this type of testing can be fine-tuned to discriminate SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. The saliva RT-PCR SYBR Green test was successfully used in a mass-screening initiative targeting nearly 4500 asymptomatic children under the age of 12. Testing was performed at a reasonable cost, and in some cases, the saliva test outperformed NP rapid antigen tests in identifying infected children. Whole genome sequencing revealed that the antigen testing failure could not be attributed to a specific lineage of SARS-CoV-2. Overall, this work strongly supports the view that RT-PCR saliva tests based on DNA-intercalating dyes represent a powerful strategy for community screening of SARS-CoV-2. The tests can be easily applied to other infectious agents and, therefore, constitute a powerful resource for an effective response to future pandemics.
Keywords: COVID-19; RT-PCR SYBR Green; diagnostics; saliva test.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical Performance of Direct RT-PCR Testing of Raw Saliva for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Individuals.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0222922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02229-22. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36409097 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance Assessment of Saliva RT-PCR and Nasopharyngeal Antigen for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Peru.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0086122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00861-22. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35867471 Free PMC article.
-
A Multiplex One-Step RT-qPCR Protocol to Detect SARS-CoV-2 in NP/OP Swabs and Saliva.Curr Protoc. 2021 May;1(5):e145. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.145. Curr Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34004070 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Self-Collected Saliva Versus Nasopharyngeal Swab for the Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in the Clinical Setting.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0046821. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00468-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34730436 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva as an alternative specimen to nasopharyngeal swabs for COVID-19 diagnosis: Review.Access Microbiol. 2022 May 20;4(5):acmi000366. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000366. eCollection 2022 Aug. Access Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36003360 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
