Editorial: Adaptation of plants to waterlogging and hypoxia
- PMID: 38835862
- PMCID: PMC11148463
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1425012
Editorial: Adaptation of plants to waterlogging and hypoxia
Keywords: carbon assimilation; climate change; crop yields; flooding; plant secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
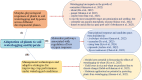
Comment on
- Editorial on the Research Topic Adaptation of plants to waterlogging and hypoxia
References
-
- Ahmad W., Ullah N., Xu L., El Sabagh A. (2022). Global food and nutrition security under changing climates. Front. Agron. 3, 799878. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2021.799878 - DOI
-
- El-Hendawy S. E., Sone C., Ito O., Sakagami J. I. (2011). Evaluation of germination ability in rice seeds under anaerobic conditions by cluster analysis. Res. J. Seed Sci. 4, 82–93. doi: 10.3923/rjss.2011.82.93 - DOI
-
- Ma S., Gai P., Wang Y., Ullah N., Zhang W., Fan Y., et al. (2021). Carbohydrate assimilation and translocation regulate grain yield formation in wheat crops (Triticum aestivum L.) under post-flowering waterlogging. Agronomy 11, 2209. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11112209 - DOI
-
- Najeeb U., Atwell B. J., Bange M. P., Tan D. K. (2015). Aminoethoxyvinylglycine (AVG) ameliorates waterlogging-induced damage in cotton by inhibiting ethylene synthesis and sustaining photosynthetic capacity. Plant Growth Regul. 76, 83–98. doi: 10.1007/s10725-015-0037-y - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

