Sitting Sideways Causes Different Femoral-Tibial Rotations in Each Knee
- PMID: 38836162
- PMCID: PMC11149726
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59678
Sitting Sideways Causes Different Femoral-Tibial Rotations in Each Knee
Abstract
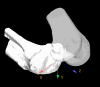
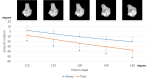
Purpose According to a previous study, asymmetrical kneeling, such as sitting sideways, does not exhibit asymmetrical movements. Rotational analyses of each femur and tibia help explain why rotational knee kinematics while sitting sideways do not exhibit asymmetrical movement. We aimed to assess the rotation of the femur and tibia in normal knees while sitting sideways. Methods Each volunteer sat sideways under fluoroscopy. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional registration techniques were used. After evaluating the femoral rotation angle relative to the tibia at each flexion angle, the femoral and tibial sole rotation angles at each flexion angle were compared between the ipsilateral and contralateral knees. Results While sitting sideways, both knees showed femoral external rotation relative to the tibia with flexion. In the ipsilateral knees, the femurs exhibited an external rotation of 26.3 ± 8.0°, from 110° to 150° of flexion. Conversely, the tibia exhibited an external rotation of 12.2 ± 7.8°, from 110° to 150° of flexion. From 110° to 150° of flexion, femoral external rotation was significantly larger than tibial external rotation. In the contralateral knees, the femurs exhibited an internal rotation of 23.8 ± 6.3°, from 110° to 150° of flexion (110°, p < 0.001; 120°, p < 0.001; 130°, p < 0.001; 140°, p < 0.001; and 150°, p < 0.001). Contrastingly, the tibia exhibited an internal rotation of 30.4 ± 8.8°, from 110° to 150° of flexion, which was significantly larger than femoral internal rotation (110°, p = 0.002; 120°, p < 0.001; 130°, p < 0.001; 140°, p < 0.001; and 150°, p < 0.001). Conclusions Although bilateral knees exhibited femoral external rotation relative to the tibia while sitting sideways, the ipsilateral and contralateral knees showed femoral and tibial sole rotations in opposite directions. In particular, the contralateral knees might show a strained movement because both femurs and tibias exhibited internal rotation with flexion. Patients who have undergone guided-motion total knee arthroplasty (TKA) or medial-pivot TKAs might be advised to avoid sitting sideways.
Keywords: axial rotation; kinematics; kneeling; normal knee; sitting sideways.
Copyright © 2024, Kono et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In Vivo three-dimensional kinematics of normal knees during sitting sideways on the floor.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Apr 6;23(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05267-z. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35387622 Free PMC article.
-
[In vitro analysis of the continuous active patellofemoral kinematics of the normal and prosthetic knee].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2002 Dec;88(8):797-802. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2002. PMID: 12503021 French.
-
In vivo three-dimensional kinematics of normal knees during different high-flexion activities.Bone Joint J. 2018 Jan;100-B(1):50-55. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B1.BJJ-2017-0553.R2. Bone Joint J. 2018. PMID: 29305450 Free PMC article.
-
Tibiofemoral articulation and axial tibial rotation of the knee after a cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024 May 24;36(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s43019-024-00224-7. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38790070 Free PMC article.
-
Prosthesis alignment affects axial rotation motion after total knee replacement: a prospective in vivo study combining computed tomography and fluoroscopic evaluations.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012 Oct 23;13:206. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-206. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012. PMID: 23088451 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- In vivo fluoroscopic analysis of the normal human knee. Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Mahfouz M. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Hip, knee, and ankle kinematics of high range of motion activities of daily living. Hemmerich A, Brown H, Smith S, Marthandam SS, Wyss UP. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:770–781. - PubMed
-
- Dynamic activity dependence of in vivo normal knee kinematics. Moro-oka TA, Hamai S, Miura H, et al. J Orthop Res. 2008;26:428–434. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
