Vascular service provision during the COVID-19 pandemic worsened major amputation rates in socially deprived diabetic populations
- PMID: 38836223
- PMCID: PMC11148210
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1304436
Vascular service provision during the COVID-19 pandemic worsened major amputation rates in socially deprived diabetic populations
Abstract
Introduction: The Coronavirus Disease - 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic significantly impacted healthcare service provision and put diabetic patients at increased risk of adverse health outcomes. We aimed to assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence and demographic shift of major lower-limb amputation in diabetic patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of diabetic patient records undergoing major lower-limb amputation between 01/03/2019 and 01/03/2021 at the Royal Sussex County Hospital, the regional arterial hub for Sussex. Primary outcomes were amputation incidence rates and patient demographics compared between the prepandemic and pandemic cohorts.
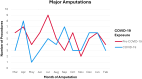
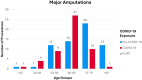
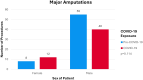
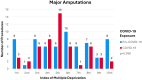
Results: The incidence rate ratio of major lower-limb amputations shows a drop in amputations during the pandemic compared to pre-pandemic (IRR 0.82; 95% CI 0.57-1.18). Data suggests a shift in the social deprivation background of patients receiving amputations to disproportionately affect those in the more deprived 50% of the population (p=0.038). Younger patients received more amputations during the pandemic compared to prepandemic levels (p=0.001).
Conclusion: Results suggest that during the COVID-19 pandemic there was a paradoxical reduction in amputations compared to prepandemic levels. However, changes to the demographic makeup of patient's receiving amputations are alarming as younger, and more deprived patients have been disproportionately affected by the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; amputation; diabetic foot; public health; social deprivation; surgical.
Copyright © 2024 AlMajali, Richards, Yusuf and Telgenkamp.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Population-Based Analysis of Diabetes-Related Care Measures, Foot Complications, and Amputation During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Ontario, Canada.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jan 4;5(1):e2142354. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42354. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 34985514 Free PMC article.
-
Major Lower-Limb Amputation During the COVID Pandemic in South India.Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2023 Sep;22(3):475-479. doi: 10.1177/15347346211020985. Epub 2021 May 28. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2023. PMID: 34047626
-
Lower Extremity Amputations Among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Five-Year Analysis in a Clinical Hospital in Bucharest, Romania.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 4;60(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/medicina60122001. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768881 Free PMC article.
-
A review of disparities in peripheral artery disease and diabetes-related amputations during the COVID-19 pandemic.Semin Vasc Surg. 2023 Mar;36(1):90-99. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2022.12.002. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Semin Vasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 36958904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia.Semin Vasc Surg. 2021 Sep;34(3):89-95. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2021.05.006. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Semin Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34642041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Pandemic on the Clinical Status of Patients Admitted to Hospital for Diabetic Foot: A Retrospective Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 17;14(14):5067. doi: 10.3390/jcm14145067. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725760 Free PMC article.
-
Trends of lower-limb complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during the COVID-19 pandemic.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2025 Aug;226:112331. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2025.112331. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 40543573
References
-
- Department of Health and Social Care. Hancock M. Health Secretary sets out government “battle plan” for COVID-19 (2020). Available online at: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/health-secretary-sets-out-government-... (Accessed March 20, 2022).
-
- Paisey RB, Abbott A, Levenson R, Harrington A, Browne D, Moore J, et al. . Diabetes-related major lower limb amputation incidence is strongly related to diabetic foot service provision and improves with enhancement of services: peer review of the South-West of England. Diabetes Med. (2017) 35:53–62. doi: 10.1111/dme.13512 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Diabetes Audit Programme . National Diabetes Audit (NDA) 2021–22 quarterly report for England, Clinical Commissioning Groups and GP practices (2022). Available online at: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/nat... (Accessed November 19, 2023).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

