Manganese(II) promotes prebiotically plausible non-enzymatic RNA ligation reactions
- PMID: 38836405
- PMCID: PMC11189027
- DOI: 10.1039/d4cc01086h
Manganese(II) promotes prebiotically plausible non-enzymatic RNA ligation reactions
Abstract
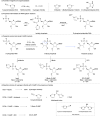
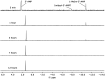
Using different prebiotically plausible activating reagents, the RNA ligation yield was significantly increased in the presence of Mn(II). The mechanism of the activation reaction has been investigated using 5'-AMP as an analogue.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prebiotically plausible oligoribonucleotide ligation facilitated by chemoselective acetylation.Nat Chem. 2013 May;5(5):383-9. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1626. Epub 2013 Apr 14. Nat Chem. 2013. PMID: 23609088 Free PMC article.
-
Prebiotically plausible mechanisms increase compositional diversity of nucleic acid sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(10):4711-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks065. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22319215 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Catalyzed RNA Ligation within Prebiotically Plausible Model Protocells.Chemistry. 2023 Aug 1;29(43):e202301376. doi: 10.1002/chem.202301376. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 37216492
-
Manganese-Oxygen Intermediates in O-O Bond Activation and Hydrogen-Atom Transfer Reactions.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Nov 21;50(11):2706-2717. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00343. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 29064667 Review.
-
From the one-carbon amide formamide to RNA all the steps are prebiotically possible.Biochimie. 2012 Jul;94(7):1451-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.02.018. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22738728 Review.
Cited by
-
Derivatization of Solid Supports Using a Carbamate-Linked Tether Containing a Disulfide Functional Group.Curr Protoc. 2025 Aug;5(8):e70174. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.70174. Curr Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40773368 Free PMC article.
-
Chirality-Promoted Chemical Ligation and Reverse Transcription of Acyclic Threoninol Nucleic Acid.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 May 28;147(21):17967-17974. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c03128. Epub 2025 Apr 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 40245353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudnick R. and Gao S., Treatise on Geochemistry, Elsevier, 2nd Edn, 2014, pp. 1–51
-
- Crerar D., Cormick R. and Barnes H., Geology and Geochemistry of Manganese, Schweizerbart, Stuttgart, 1980, pp. 293–334
-
- Stumm W. and Morgan J. J., Aquatic chemistry: Chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1996
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

