The Contribution of Meckel's Cartilage-Derived Type II Collagen-Positive Cells to the Jawbone Development and Repair
- PMID: 38836522
- PMCID: PMC11179589
- DOI: 10.1369/00221554241259059
The Contribution of Meckel's Cartilage-Derived Type II Collagen-Positive Cells to the Jawbone Development and Repair
Abstract
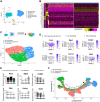
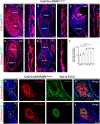
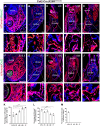
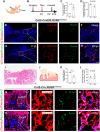
Jawbones and long bones, despite their shared skeletal lineage, frequently exhibit distinct origins and developmental pathways. Identifying specific progenitor subsets for mandibular osteogenesis remains challenging. Type II collagen is conventionally associated with cartilaginous structures, yet our investigation has identified the presence of type II collagen positive (Col2+) cells within the jawbone development and regeneration. The role of Col2+ cells in jawbone morphogenesis and repair has remained enigmatic. In this study, we analyze single-cell RNA sequencing data from mice jawbone at embryonic day 10.5. Through fate-mapping experiments, we have elucidated that Col2+ cells and their progeny are instrumental in mandibular osteogenesis across both fetal and postnatal stages. Furthermore, lineage tracing with a tamoxifen-inducible CreER system has established the pivotal role of Col2+ cells, marked by Col2-CreER and originating from the primordial Meckel's cartilage, in jawbone formation. Moreover, our research explored models simulating jawbone defects and tooth extraction, which underscored the osteogenic differentiation capabilities of postnatal Col2+ cells during repair. This finding not only highlights the regenerative potential of Col2+ cells but also suggests their versatility in contributing to skeletal healing and regeneration. In conclusion, our findings position Col2+ cells as essential in orchestrating osteogenesis throughout the continuum of mandibular development and repair.
Keywords: Col2; jawbone; lineage tracing; mandibular osteogenesis; osteogenic differentiation; progenitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type II collagen-positive embryonic progenitors are the major contributors to spine and intervertebral disc development and repair.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 Oct;10(10):1419-1432. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0424. Epub 2021 May 25. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34032373 Free PMC article.
-
Type II collagen-positive progenitors are important stem cells in controlling skeletal development and vascular formation.Bone Res. 2022 Jun 23;10(1):46. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00214-z. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 35739091 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Periosteal Osteogenic Progenitors in Jawbone.J Dent Res. 2022 Aug;101(9):1101-1109. doi: 10.1177/00220345221084200. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Dent Res. 2022. PMID: 35319300
-
Skeletal stem and progenitor cells in bone development and repair.J Bone Miner Res. 2024 Jul 23;39(6):633-654. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjae069. J Bone Miner Res. 2024. PMID: 38696703 Review.
-
Osteoblast recruitment to sites of bone formation in skeletal development, homeostasis, and regeneration.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013 Sep;99(3):170-91. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21047. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013. PMID: 24078495 Review.
References
-
- Chai Y, Maxson RE., Jr. Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev Dyn. 2006;235(9):2353–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

