Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Adults and Children With Medically Attended Acute Respiratory Illness Over Three Seasons
- PMID: 38836601
- PMCID: PMC12187053
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciae303
Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Adults and Children With Medically Attended Acute Respiratory Illness Over Three Seasons
Abstract
Background: Data on the true prevalence of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) among medically attended acute respiratory illnesses (MAARI) has been limited by the lack of regular clinical testing of mild to moderate illnesses. Here we present a prospective evaluation of the epidemiology of RSV-associated MAARI across age groups and multimorbidity status over 3 seasons, which is informative in light of the recommendations for shared decision making for vaccination in older adults.
Methods: Ambulatory patients ≥6 months of age meeting a common MAARI case definition were prospectively enrolled in the Michigan Ford Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness (MFIVE) study, a subsite of the US Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network. All participants were tested by nasal-throat swab for RSV and influenza, including subtype, independently from clinician-directed testing. Participant illness characteristics and calculated multimorbidity-weighted index (MWI) were collected by in-person survey and electronic medical record review.
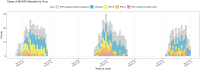
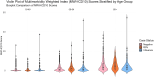
Results: Over 3 surveillance seasons (fall 2017 to spring 2020), 9.9% (n = 441) of 4442 participants had RSV detected. RSV-associated MAARI was more prevalent than influenza for participants 6 months to 4 years of age. Adults with RSV-MAARI had higher median MWI scores overall compared to influenza-MAARI and controls with neither virus (1.62, 0.40, and 0.64, respectively).
Conclusions: RSV is a significant, underrecognized cause of MAARI in both children and adults presenting for ambulatory care. Multimorbidity is an important contributor to RSV-associated MAARI in outpatient adults, providing information to support shared clinical decision making for vaccination.
Keywords: adult; child; medically-attended acute respiratory illness; multimorbidity; respiratory syncytial virus.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. E. T. M. has received research funding from Merck related to the submitted work. L. L. has received consulting fees from Janssen paid to institution. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Falsey AR, Hennessey PA, Formica MA, Cox C, Walsh EE. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med 2005; 352:1749–59. - PubMed
-
- Walsh EE, Peterson DR, Falsey AR. Risk factors for severe respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly persons. J Infect Dis 2004; 189:233–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

