Legionella effectors SidC/SdcA ubiquitinate multiple small GTPases and SNARE proteins to promote phagosomal maturation
- PMID: 38836877
- PMCID: PMC11335287
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05271-7
Legionella effectors SidC/SdcA ubiquitinate multiple small GTPases and SNARE proteins to promote phagosomal maturation
Abstract
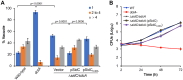
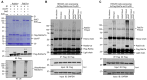
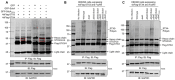
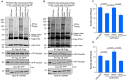
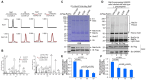
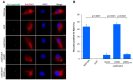
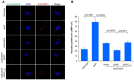
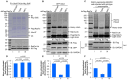
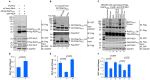
Protein ubiquitination is one of the most important posttranslational modifications (PTMs) in eukaryotes and is involved in the regulation of almost all cellular signaling pathways. The intracellular bacterial pathogen Legionella pneumophila translocates at least 26 effectors to hijack host ubiquitination signaling via distinct mechanisms. Among these effectors, SidC/SdcA are novel E3 ubiquitin ligases with the adoption of a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad. SidC/SdcA are critical for the recruitment of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived vesicles to the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV). However, the ubiquitination targets of SidC/SdcA are largely unknown, which restricts our understanding of the mechanisms used by these effectors to hijack the vesicle trafficking pathway. Here, we demonstrated that multiple Rab small GTPases and target soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNARE) proteins are bona fide ubiquitination substrates of SidC/SdcA. SidC/SdcA-mediated ubiquitination of syntaxin 3 and syntaxin 4 promotes their unconventional pairing with the vesicle-SNARE protein Sec22b, thereby contributing to the membrane fusion of ER-derived vesicles with the phagosome. In addition, our data reveal that ubiquitination of Rab7 by SidC/SdcA is critical for its association with the LCV membrane. Rab7 ubiquitination could impair its binding with the downstream effector Rab-interacting lysosomal protein (RILP), which partially explains why LCVs avoid fusion with lysosomes despite the acquisition of Rab7. Taken together, our study reveals the biological mechanisms employed by SidC/SdcA to promote the maturation of the LCVs.
Keywords: Effector proteins; Legionella pneumophila; RILP; Rab small GTPase; SNARE proteins; Ubiquitination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Legionella pneumophila promotes functional interactions between plasma membrane syntaxins and Sec22b.Traffic. 2010 May;11(5):587-600. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01050.x. Epub 2010 Feb 15. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20163564 Free PMC article.
-
The Legionella effector SidC defines a unique family of ubiquitin ligases important for bacterial phagosomal remodeling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 22;111(29):10538-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402605111. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25006264 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Legionella Virulence Factor, SidC Reveals a Unique PI(4)P-Specific Binding Domain Essential for Its Targeting to the Bacterial Phagosome.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jun 12;11(6):e1004965. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004965. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26067986 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting the ubiquitin and phosphoinositide pathways by the Legionella pneumophila effector, SidC.Curr Genet. 2016 Feb;62(1):105-8. doi: 10.1007/s00294-015-0521-y. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Curr Genet. 2016. PMID: 26433729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution and Adaptation of Legionella pneumophila to Manipulate the Ubiquitination Machinery of Its Amoebae and Mammalian Hosts.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 15;11(1):112. doi: 10.3390/biom11010112. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33467718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Canonical and phosphoribosyl ubiquitination coordinate to stabilize a proteinaceous structure surrounding the Legionella-containing vacuole.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 23:2025.07.22.666189. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.22.666189. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40777347 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

