The effectiveness of mind-body therapy and physical training in alleviating depressive symptoms in adult cancer patients: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 38836958
- PMCID: PMC11153279
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05813-3
The effectiveness of mind-body therapy and physical training in alleviating depressive symptoms in adult cancer patients: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to assess the effectiveness of mind-body therapy (MBT) and/or physical training in alleviating depressive symptoms among adult cancer patients through a meta-analysis.
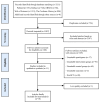
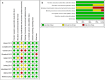
Methods: PubMed, Embase, EBSCO, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were searched from up to October 21, 2023. Effect sizes, 95% confidence intervals, and other pertinent values were computed utilizing a random-effects model with Review Manager 5.3 and StataMP 14. The reporting of findings adhered to the guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The PROSPERO registration code for this review is 4,203,477,316.
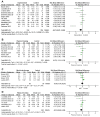
Results: 10 randomized controlled trials (11 datasets) involving a total of 620 participants were selected for analysis. The results demonstrated that complementary therapies, encompassing MBT and physical training, were effective in alleviating depressive symptoms in adult cancer patients (SMD= -0.47; 95%CI: -0.87, -0.08; P = 0.02). Subgroup analysis indicate that physical training may effectively alleviate depressive symptoms (SMD= -0.72; 95%CI: -1.31, -0.13; P = 0.02), demonstrating moderate effect sizes. Conversely, MBT does not seem to significantly influence depressive symptoms (P = 0.69).
Conclusions: Complementary therapy lasting four weeks or more, incorporating physical training and MBT, has been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms in adult cancer patients. And physical training has a significant effect on depressive symptoms, while MBT has no effect. Nevertheless, given the constraints of the included studies, further research is required in the future to provide more robust evidence.
Keywords: Adult; Cancer; Depression; Mind-body therapy; Physical training.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exercise interventions on health-related quality of life for people with cancer during active treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD008465. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008465.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895974 Free PMC article.
-
Mind and body therapy for fibromyalgia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 9;2015(4):CD001980. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001980.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25856658 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological therapies for treatment-resistant depression in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 14;5(5):CD010558. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010558.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29761488 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Prebiotics and Probiotics on Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety in Clinically Diagnosed Samples: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Nutr Rev. 2025 Jul 1;83(7):e1504-e1520. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuae177. Nutr Rev. 2025. PMID: 39731509 Free PMC article.
-
Couple therapy for depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 8;6(6):CD004188. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004188.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29882960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caruso R, Nanni MG, Riba M et al (2017a) Depressive spectrum disorders in cancer: prevalence, risk factors and screening for depression: a critical review. Acta Oncol 56:146–155. 10.1080/0284186X.2016.1266090 - PubMed
-
- Caruso R, Nanni MG, Riba MB et al (2017b) The burden of psychosocial morbidity related to cancer: patient and family issues. Int Rev Psychiatry 29:389–402. 10.1080/09540261.2017.1288090 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No.2022YFC3600201/the National Key R&D Program of China
- No.2022YFC3600201/the National Key R&D Program of China
- No.2022YFC3600201/the National Key R&D Program of China
- No.2022YFC3600201/the National Key R&D Program of China
- Z2022019/the project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission: Study of MTT Exercise Rehabilitation Training for Community Elderly with Muscle Attenuation Syndrome Based on the IOT Cloud Platform
- Z2022019/the project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission: Study of MTT Exercise Rehabilitation Training for Community Elderly with Muscle Attenuation Syndrome Based on the IOT Cloud Platform
- Z2022019/the project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission: Study of MTT Exercise Rehabilitation Training for Community Elderly with Muscle Attenuation Syndrome Based on the IOT Cloud Platform
- Z2022019/the project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission: Study of MTT Exercise Rehabilitation Training for Community Elderly with Muscle Attenuation Syndrome Based on the IOT Cloud Platform
- Q202241/the Wuxi Municipal Health Commission Youth Project: Study on the clinical application of exercise rehabilitation to prevent falls in community-dwelling elderly with muscle wasting syndrome
- Q202241/the Wuxi Municipal Health Commission Youth Project: Study on the clinical application of exercise rehabilitation to prevent falls in community-dwelling elderly with muscle wasting syndrome
- Q202241/the Wuxi Municipal Health Commission Youth Project: Study on the clinical application of exercise rehabilitation to prevent falls in community-dwelling elderly with muscle wasting syndrome
- Q202241/the Wuxi Municipal Health Commission Youth Project: Study on the clinical application of exercise rehabilitation to prevent falls in community-dwelling elderly with muscle wasting syndrome
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

