Exploring the potential of isorhapontigenin: attenuating Staphylococcus aureus virulence through MgrA-mediated regulation
- PMID: 38837389
- PMCID: PMC11332347
- DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00317-24
Exploring the potential of isorhapontigenin: attenuating Staphylococcus aureus virulence through MgrA-mediated regulation
Abstract
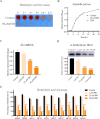
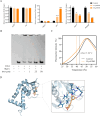
The emerging prevalence of drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates underscores the urgent need for alternative therapeutic strategies due to the declining effectiveness of traditional antibiotics in clinical settings. MgrA, a key virulence regulator in S. aureus, orchestrates the expression of numerous virulence factors. Here, we report the discovery of isorhapontigenin, a methoxylated analog of resveratrol, as a potential anti-virulence agent against S. aureus. Isorhapontigenin effectively inhibits the hemolytic activity of S. aureus in a non-bactericidal manner. Additionally, it significantly reduces the cytotoxicity of S. aureus and impairs its ability to survive in macrophages. Mechanistically, isorhapontigenin modulates the expression of virulence factors, dose-dependently downregulating hla and upregulating the MgrA-regulated gene spa. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated that isorhapontigenin inhibits the binding of MgrA to the hla promoter in a dose-dependent manner. Thermal shift assays confirmed the direct interaction between isorhapontigenin and the MgrA protein. The in vivo experiments demonstrated that isorhapontigenin significantly reduced the area of skin abscesses and improved survival in a pneumonia model while decreasing bacterial burden and inflammation in the lungs. In conclusion, isorhapontigenin holds potential as a candidate drug for further development as an anti-virulence agent for treating S. aureus infections.
Importance: The emergence of antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains presents a formidable challenge to public health, necessitating novel approaches in combating these pathogens. Traditional antibiotics are becoming increasingly ineffective, leading to a pressing need for innovative therapeutic strategies. In this study, targeting virulence factors that play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of bacterial infections offers a promising alternative to circumvent resistance mechanisms. The discovery of isorhapontigenin as an inhibitor of S. aureus virulence represents a significant advance in anti-virulence therapy.
Keywords: MgrA; Staphylococcus aureus; isorhapontigenin; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elucidating the potential of isorhapontigenin in targeting the MgrA regulatory network: a paradigm shift for attenuating MRSA virulence.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Sep 4;68(9):e0061124. doi: 10.1128/aac.00611-24. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 39046236 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MgrA-mediated virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus.Chem Biol. 2011 Aug 26;18(8):1032-41. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.05.014. Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21867918 Free PMC article.
-
Uncariitannin, a polyphenolic polymer from Uncaria gambier, attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence through an MgrA-mediated regulation of α-hemolysin.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Sep;147:104328. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104328. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31288080
-
High-Throughput Screening Strategies for the Development of Anti-Virulence Inhibitors Against Staphylococcus aureus.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(13):2297-2312. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666171121102829. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29165063 Review.
-
Disarming Staphylococcus aureus: Review of Strategies Combating This Resilient Pathogen by Targeting Its Virulence.Pathogens. 2025 Apr 15;14(4):386. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14040386. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40333163 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isorhapontigenin: exploring a promising resveratrol analog for disease management through diverse signaling pathways-a review with computational insights.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04176-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40244453 Review.
References
-
- Algammal AM, Hetta HF, Elkelish A, Alkhalifah DHH, Hozzein WN, Batiha GE-S, El Nahhas N, Mabrok MA. 2020. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): one health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect Drug Resist 13:3255–3265. doi:10.2147/IDR.S272733 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
