Genomic investigation and clinical correlates of the in vitro β-lactam: NaHCO3 responsiveness phenotype among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38837393
- PMCID: PMC11232399
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00218-24
Genomic investigation and clinical correlates of the in vitro β-lactam: NaHCO3 responsiveness phenotype among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
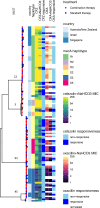
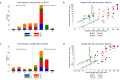
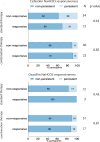
NaHCO3 responsiveness is a novel phenotype where some methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates exhibit significantly lower minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) to oxacillin and/or cefazolin in the presence of NaHCO3. NaHCO3 responsiveness correlated with treatment response to β-lactams in an endocarditis animal model. We investigated whether treatment of NaHCO3-responsive strains with β-lactams was associated with faster clearance of bacteremia. The CAMERA2 trial (Combination Antibiotics for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus) randomly assigned participants with MRSA bloodstream infections to standard therapy, or to standard therapy plus an anti-staphylococcal β-lactam (combination therapy). For 117 CAMERA2 MRSA isolates, we determined by broth microdilution the MIC of cefazolin and oxacillin, with and without 44 mM of NaHCO3. Isolates exhibiting ≥4-fold decrease in the MIC to cefazolin or oxacillin in the presence of NaHCO3 were considered "NaHCO3-responsive" to that agent. We compared the rate of persistent bacteremia among participants who had infections caused by NaHCO3-responsive and non-responsive strains, and that were assigned to combination treatment with a β-lactam. Thirty-one percent (36/117) and 25% (21/85) of MRSA isolates were NaHCO3-responsive to cefazolin and oxacillin, respectively. The NaHCO3-responsive phenotype was significantly associated with sequence type 93, SCCmec type IVa, and mecA alleles with substitutions in positions -7 and -38 in the regulatory region. Among participants treated with a β-lactam, there was no association between the NaHCO3-responsive phenotype and persistent bacteremia (cefazolin, P = 0.82; oxacillin, P = 0.81). In patients from a randomized clinical trial with MRSA bloodstream infection, isolates with an in vitro β-lactam-NaHCO3-responsive phenotype were associated with distinctive genetic signatures, but not with a shorter duration of bacteremia among those treated with a β-lactam.
Keywords: MRSA; bacterial genomics; bloodstream-infections; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3); β-lactams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kourtis AP, Hatfield K, Baggs J, Mu Y, See I, Epson E, Nadle J, Kainer MA, Dumyati G, Petit S, Ray SM, Ham D, Capers C, Ewing H, Coffin N, McDonald LC, Jernigan J, Cardo D, Emerging Infections Program MRSA author group . 2019. Vital signs: epidemiology and recent trends in methicillin-resistant and in methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections - United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 68:214–219. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6809e1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McDanel JS, Perencevich EN, Diekema DJ, Herwaldt LA, Smith TC, Chrischilles EA, Dawson JD, Jiang L, Goto M, Schweizer ML. 2015. Comparative effectiveness of beta-lactams versus vancomycin for treatment of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections among 122 hospitals. Clin Infect Dis 61:361–367. doi:10.1093/cid/civ308 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, Rybak MJ, Talan DA, Chambers HF. 2011. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis 52:e18–e55. doi:10.1093/cid/ciq146 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

