Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Enable Incompatible Blood Transfusions
- PMID: 38837643
- PMCID: PMC11304279
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202310230
Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Enable Incompatible Blood Transfusions
Abstract
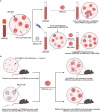
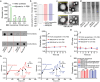
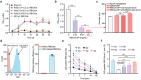
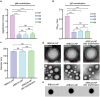
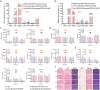
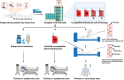
Blood transfusions save lives and improve health every day. Despite the matching of blood types being stricter than it ever has been, emergency transfusions among incompatible blood types are still inevitable in the clinic when there is a lack of acceptable blood types for recipients. Here to overcome this, a counter measure nanoplatform consisting of a polymeric core coated by a red blood cell (RBC) membrane is developed. With A-type or B-type RBC membrane camouflaging, the nanoplatform is capable of specifically capturing anti-A or anti-B IgM antibodies within B-type or A-type whole blood, thereby decreasing the corresponding IgM antibody levels and then allowing the incompatible blood transfusions. In addition to IgM, the anti-RBC IgG antibody in a passive immunization murine model can likewise be neutralized by this nanoplatform, leading to prolonged circulation time of incompatible donor RBCs. Noteworthily, nanoplatform made by expired RBCs (>42 days stored hypothermically) and then subjected to lyophilization does not impair their effect on antibody neutralization. Most importantly, antibody-captured RBC-NP do not exacerbate the risk of inflammation, complement activation, and coagulopathy in an acute hemorrhagic shock murine model. Overall, this biomimetic nanoplatform can safely neutralize the antibody to enable incompatible blood transfusion.
Keywords: antibody; biomimetic nanoparticle; cell membrane; incompatible blood transfusion; neutralization.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fahimnia B., Jabbarzadeh A., Ghavamifar A., Bell M., Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 700.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- LR22H150001/Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation
- WKJ-ZJ-2339/Key Projects Jointly Constructed by Zhejiang Province and the Ministry
- 2021ZY0002/Major Innovation Project of Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau
- 2023J037/Key Project of Ningbo Science and Technology Bureau
- LTGY23H040006/Project of Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
