Activation of the Mevalonate Pathway in Response to Anti-cancer Treatments Drives Glioblastoma Recurrences Through Activation of Rac-1
- PMID: 38837899
- PMCID: PMC11197925
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0049
Activation of the Mevalonate Pathway in Response to Anti-cancer Treatments Drives Glioblastoma Recurrences Through Activation of Rac-1
Abstract
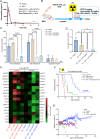
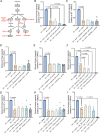
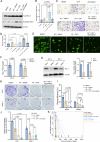
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the deadliest adult brain cancer. Under the current standard of care, almost all patients succumb to the disease and novel treatments are urgently needed. Recognizing that GBMs are addicted to cholesterol, past clinical trials have repurposed statins against GBM but failed. The purpose of this study was to test whether treatments that upregulate the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway in GBM would generate a metabolic vulnerability that can be exploited using statins and to determine the underlying mechanisms.Effects of radiotherapy and temozolomide or dopamine receptor antagonists on the mevalonate pathway in GBM were assessed in vitro and in vivo. The impact of statins on self-renewal of glioma stem cells and median survival was studied. Branches of the mevalonate pathway were probed to identify relevant effector proteins.Cells surviving combination treatments that converge in activating the immediate early response, universally upregulated the mevalonate pathway and increased stemness of GBM cells through activation of the Rho-GTPase Rac-1. Activation of the mevalonate pathway and Rac-1 was inhibited by statins, which led to improved survival in mouse models of glioblastoma when combined with radiation and drugs that target the glioma stem cell pool and plasticity of glioma cells.We conclude that a combination of dopamine receptor antagonists and statins could potentially improve radiotherapy outcome and warrants further investigation.
Significance: Combination therapies that activate the mevalonate pathway in GBM cells after sublethal treatment enhance self-renewal and migratory capacity through Rac-1 activation, which creates a metabolic vulnerability that can be further potentially exploited using statins.
© 2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



Update of
-
Activation of the mevalonate pathway in response to anti-cancer treatments drives glioblastoma recurrences through activation of Rac-1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 25:2023.07.23.550205. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.23.550205. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cancer Res Commun. 2024 Jun 25;4(6):1566-1580. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0049. PMID: 37546917 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Activation of the mevalonate pathway in response to anti-cancer treatments drives glioblastoma recurrences through activation of Rac-1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 25:2023.07.23.550205. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.23.550205. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cancer Res Commun. 2024 Jun 25;4(6):1566-1580. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0049. PMID: 37546917 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Afatinib and Temozolomide combination inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting EGFRvIII-cMet signaling in glioblastoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 18;38(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1264-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31215502 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin Augments the Chemosensitivity of Human Glioma Cells to Temozolomide by Activating AMPK and Inhibiting the AKT Signaling Pathway.Mol Pharm. 2018 Nov 5;15(11):4912-4925. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00551. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30336060
-
Could drugs inhibiting the mevalonate pathway also target cancer stem cells?Drug Resist Updat. 2016 Mar;25:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Drug Resist Updat. 2016. PMID: 27155373 Review.
-
The Importance of Tumor Stem Cells in Glioblastoma Resistance to Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 8;22(8):3863. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083863. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on cholesterol metabolism and tumor therapy.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 30;16(1):647. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02430-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40307614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect and related mechanisms of RAC1 GTP on radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30;14(6):3772-3784. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-987. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40687217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eramo A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Zeuner A, Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G, et al. . Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Death Differ 2006;13:1238–41. - PubMed
-
- Bao S. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006;444:756–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA281682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA260886/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P50CA211015/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01CA200234/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA200234/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DISC2-14083/California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM)
- R01CA281682/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P50 CA211015/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA260886/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03CA289852/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R03 CA289852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

