Comparative analysis of Bcl-2 family protein overexpression in CAR T cells alone and in combination with BH3 mimetics
- PMID: 38838132
- PMCID: PMC11737343
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adk7640
Comparative analysis of Bcl-2 family protein overexpression in CAR T cells alone and in combination with BH3 mimetics
Abstract
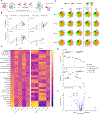
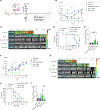
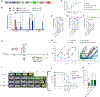
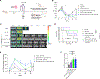
Approximately 50% of patients with hematologic malignancies relapse after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell treatment; mechanisms of failure include loss of CAR T persistence and tumor resistance to apoptosis. We hypothesized that both of these challenges could potentially be overcome by overexpressing one or more of the Bcl-2 family proteins in CAR T cells to reduce their susceptibility to apoptosis, both alone and in the presence of BH3 mimetics, which can be used to activate apoptotic machinery in malignant cells. We comprehensively investigated overexpression of different Bcl-2 family proteins in CAR T cells with different signaling domains as well as in different tumor types. We found that Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 overexpression in CAR T cells bearing a 4-1BB costimulatory domain resulted in increased expansion and antitumor activity, reduced exhaustion, and decreased apoptotic priming. In addition, CAR T cells expressing either Bcl-xL or a venetoclax-resistant Bcl-2 variant led to enhanced antitumor efficacy and survival in murine xenograft models of lymphoma and leukemia in the presence or absence of the BH3 mimetic venetoclax, a clinically approved BH3 mimetic. In this setting, Bcl-xL overexpression had stronger effects than overexpression of Bcl-2 or the Bcl-2(G101V) variant. These findings suggest that CAR T cells could be optimally engineered by overexpressing Bcl-xL to enhance their persistence while opening a therapeutic window for combination with BH3 mimetics to prime tumors for apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
FK and MVM are inventors on provisional patent applications on technologies described herein, held by Massachusetts General Hospital. MVM is an inventor on patents related to adoptive cell therapies, held by Massachusetts General Hospital (some licensed to Promab) and University of Pennsylvania (some licensed to Novartis). MVM has served as a consultant for multiple companies involved in cell therapies. MVM holds Equity in 2SeventyBio, Century Therapeutics, Neximmune, Oncternal, and TCR2 and serves on the Board of Directors of 2Seventy Bio. AL has consulted for and has received research support from AbbVie, Novartis, and Astra-Zeneca. He is an equity holder and co-founder of Flash Therapeutics, and an advisor for Dialectic Therapeutics, Zentalis Pharmaceuticals, and Anji Onco. All other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Locke FL, et al., Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med, 2022. 386(7): p. 640–654. - PubMed
-
- Bishop MR, et al., Second-Line Tisagenlecleucel or Standard Care in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med, 2022. 386(7): p. 629–639. - PubMed
-
- FDA approves axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line treatment for large-b-cell-lymphoma.
-
- FDA approves lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line treatment for large-b-cell-lymphoma. - PubMed
-
- Chong EA, et al., Five-Year Outcomes for Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas with CAR T-Cell Therapy. N Engl J Med, 2021. 384(7): p. 673–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

