Genome Sequencing for Diagnosing Rare Diseases
- PMID: 38838312
- PMCID: PMC11350637
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2314761
Genome Sequencing for Diagnosing Rare Diseases
Abstract
Background: Genetic variants that cause rare disorders may remain elusive even after expansive testing, such as exome sequencing. The diagnostic yield of genome sequencing, particularly after a negative evaluation, remains poorly defined.
Methods: We sequenced and analyzed the genomes of families with diverse phenotypes who were suspected to have a rare monogenic disease and for whom genetic testing had not revealed a diagnosis, as well as the genomes of a replication cohort at an independent clinical center.
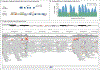
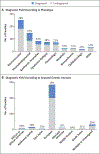
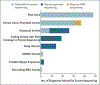
Results: We sequenced the genomes of 822 families (744 in the initial cohort and 78 in the replication cohort) and made a molecular diagnosis in 218 of 744 families (29.3%). Of the 218 families, 61 (28.0%) - 8.2% of families in the initial cohort - had variants that required genome sequencing for identification, including coding variants, intronic variants, small structural variants, copy-neutral inversions, complex rearrangements, and tandem repeat expansions. Most families in which a molecular diagnosis was made after previous nondiagnostic exome sequencing (63.5%) had variants that could be detected by reanalysis of the exome-sequence data (53.4%) or by additional analytic methods, such as copy-number variant calling, to exome-sequence data (10.8%). We obtained similar results in the replication cohort: in 33% of the families in which a molecular diagnosis was made, or 8% of the cohort, genome sequencing was required, which showed the applicability of these findings to both research and clinical environments.
Conclusions: The diagnostic yield of genome sequencing in a large, diverse research cohort and in a small clinical cohort of persons who had previously undergone genetic testing was approximately 8% and included several types of pathogenic variation that had not previously been detected by means of exome sequencing or other techniques. (Funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute and others.).
Copyright © 2024 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R00 DE026824/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U54HD090255/National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- APP1048816/National Health and Medical Research Council
- U54 HD090255/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- (funder DOI 10.13039/100014989) grants 2019-199278/Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
- DAF2019-19927/Chan Zuckerberg Initiative
- R21HG012397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008900/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY026904/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- APP1074954/National Health and Medical Research Council
- RC2 DK122397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH115957/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00DE026824/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- PUTJD827/Eesti Teadusagentuur
- R01HD081256/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- APP1106084/National Health and Medical Research Council
- R01HD105266/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- MC-2014-11-1/McLaughlin Centre, University of Toronto
- P50 HD105351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Early Career Award/Thrasher Research Fund
- PRG2040/Eesti Teadusagentuur
- APP1136197/National Health and Medical Research Council
- T32 HG010464/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- APP2007769/National Health and Medical Research Council
- K23HD102589/National Institute of Child Health and Human Development
- EGI-GE-1218-0753-UCSD/FFB/Foundation Fighting Blindness/United States
- R01 HD114353/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009141/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- Building the Next Generation Grant/CIHR/Canada
- 1DH1813319/Dietmar Hopp Stiftung
- MOBTP175/Eesti Teadusagentuur
- 5RC-2DK122397/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG009141/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- MC-2012-13/McLaughlin Centre, University of Toronto
- R01 HD081256/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD105266/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY012910/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1HG008900/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE031261/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD102589/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011755/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014104/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Fund for Medical Discovery/Massachusetts General Hospital
- R21 HG012397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- PRG471/Eesti Teadusagentuur
- U01HG011755/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- APP2002640/National Health and Medical Research Council
- APP1080587/National Health and Medical Research Council
- MC-2017-12/McLaughlin Centre, University of Toronto
- R01MH115957/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- PSG774/Eesti Teadusagentuur
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
