Impact of Prosigna test on adjuvant treatment decision in lymph node-negative early breast cancer-a prospective national multicentre study (EMIT-1)
- PMID: 38838499
- PMCID: PMC11190479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103475
Impact of Prosigna test on adjuvant treatment decision in lymph node-negative early breast cancer-a prospective national multicentre study (EMIT-1)
Abstract
Background: EMIT-1 is a national, observational, single-arm trial designed to assess the value of the Prosigna, Prediction Analysis of Microarray using the 50 gene classifier (PAM50)/Risk of Recurrence (ROR), test as a routine diagnostic tool, examining its impact on adjuvant treatment decisions, clinical outcomes, side-effects and cost-effectiveness. Here we present the impact on treatment decisions.
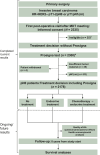
Patients and methods: Patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative pT1-pT2 lymph node-negative early breast cancer (EBC) were included. The Prosigna test and standard histopathology assessments were carried out. Clinicians' treatment decisions were recorded before (pre-Prosigna) and after (post-Prosigna) the Prosigna test results were disclosed.
Results: Of 2217 patients included, 2178 had conclusive Prosigna results. The pre-Prosigna treatment decisions were: no systemic treatment (NT) in 27% of patients, endocrine treatment alone (ET) in 38% and chemotherapy (CT) followed by ET (CT + ET) in 35%. Post-Prosigna treatment decisions were 25% NT, 51% ET and 24% CT + ET, respectively. Adjuvant treatment changed in 28% of patients, including 21% change in CT use. Among patients assigned to CT + ET pre-Prosigna, 45% were de-escalated to ET post-Prosigna. Of patients assigned to ET, 12% were escalated to CT + ET and 8% were de-escalated to NT; of those assigned to NT, 18% were escalated to ET/CT + ET. CT was more frequently recommended for patients aged ≤50 years. In the subgroup with pT1c-pT2 G2 and intermediate Ki67 (0.5-1.5× local laboratory median Ki67 score), the pre-Prosigna CT treatment decision varied widely across hospitals (3%-51%). Post-Prosigna, the variability of CT use was markedly reduced (8%-24%). The correlation between Ki67 and ROR score within this subgroup was poor (r = 0.25-0.39). The median ROR score increased by increasing histological grade, but the ROR score ranges were wide (for G1 0-79, G2 0-90, G3 16-94).
Conclusion: The Prosigna test result changed adjuvant treatment decisions in all EBC clinical risk groups, markedly decreased the CT use for patients categorized as higher clinical risk pre-Prosigna and reduced treatment decision discrepancies between hospitals.
Keywords: Prosigna; adjuvant treatment; chemotherapy; decision impact; early breast cancer; endocrine treatment.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Carter C.L., Allen C., Henson D.E. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989;63(1):181–187. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes W.D., Reis-Filho J.S., Narod S.A. Tumor size and survival in breast cancer--a reappraisal. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7(6):348–353. - PubMed
-
- Christiansen P., Bjerre K., Ejlertsen B., et al. Mortality rates among early-stage hormone receptor-positive breast cancer patients: a population-based cohort study in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103(18):1363–1372. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365(9472):1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Goldhirsch A., Wood W.C., Gelber R.D., et al. Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(7):1133–1144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

