Relationship between Pulmonary Gas Exchange Function and Brain Uptake Dynamics Investigated with Hyperpolarized 129Xe MR Imaging and Spectroscopy in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 38839300
- PMCID: PMC12406161
- DOI: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2024-0030
Relationship between Pulmonary Gas Exchange Function and Brain Uptake Dynamics Investigated with Hyperpolarized 129Xe MR Imaging and Spectroscopy in a Murine Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
Purpose: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a complex multisystem disease associated with comorbidities outside the lungs. The aim of this study was to measure changes in metrics of pulmonary gas exchange function and brain tissue metabolism in a mouse model of COPD using hyperpolarized 129Xe (HP 129Xe) MRI/MR spectroscopy (MRS) and investigate the relationship between the metrics of lung and brain.
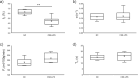
Methods: COPD phenotypes were induced in 15 mice by 6-week administration of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). A separate negative control (NC) group was formed of 6 mice administered with saline for 6 weeks. After these 6-week administrations, the pulmonary gas exchange function parameter fD (%) and the rate constant, α (s-1), which are composed of the cerebral blood flow Fi and the longitudinal relaxation rate 1/T1i in brain tissue, were evaluated by HP 129Xe MRI/MRS.
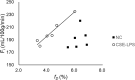
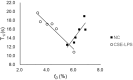
Results: The fD of CSE-LPS mice was significantly lower than that of NC mice, which was in parallel with an increase in bronchial wall thickness. The α in the CSE-LPS mice decreased with the decrease of fD in contrast to the trend in the NC mice. To further elucidate the opposed trend, the contribution of T1i was separately determined by measuring Fi. The T1i in the CSE-LPS mice was found to correlate negatively with fD as opposed to the positive trend in the NC mice. The opposite trend in T1i between CSE-LPS and NC mice suggests hypoxia in the brain, which is induced by the impaired oxygen uptake as indicated by the reduced fD.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the feasibility of using HP 129Xe MRI/MRS to study pathological mechanisms of brain dysfunction in comorbidities with COPD.
Keywords: brain uptake dynamics; hyperpolarized 129Xe; murine chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; pulmonary gas exchange function.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Combining hyperpolarized 129Xe MR imaging and spectroscopy to noninvasively estimate pulmonary vascular resistance.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025 Mar 1;138(3):623-633. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00440.2024. Epub 2025 Jan 28. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025. PMID: 39873409 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Hyperpolarized Pulmonary Functional 129 Xe MR for Long-COVID.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Apr;59(4):1120-1134. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28940. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37548112
-
Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI and Spectroscopy: Quantitative Measurements, Results, and Emerging Opportunities.Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2025 Aug;7(4):e240562. doi: 10.1148/ryct.240562. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40772846 Review.
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
-
Role and mechanism of benzo[a]pyrene in the transformation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease into lung adenocarcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul;149(8):4741-4760. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04353-y. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36229541 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

