Bilateral gene therapy in children with autosomal recessive deafness 9: single-arm trial results
- PMID: 38839897
- PMCID: PMC11271389
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03023-5
Bilateral gene therapy in children with autosomal recessive deafness 9: single-arm trial results
Abstract
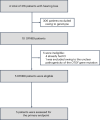
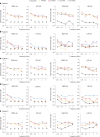
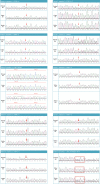
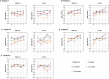
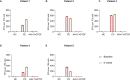
Gene therapy is a promising approach for hereditary deafness. We recently showed that unilateral AAV1-hOTOF gene therapy with dual adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 1 carrying human OTOF transgene is safe and associated with functional improvements in patients with autosomal recessive deafness 9 (DFNB9). The protocol was subsequently amended and approved to allow bilateral gene therapy administration. Here we report an interim analysis of the single-arm trial investigating the safety and efficacy of binaural therapy in five pediatric patients with DFNB9. The primary endpoint was dose-limiting toxicity at 6 weeks, and the secondary endpoint included safety (adverse events) and efficacy (auditory function and speech perception). No dose-limiting toxicity or serious adverse event occurred. A total of 36 adverse events occurred. The most common adverse events were increased lymphocyte counts (6 out of 36) and increased cholesterol levels (6 out of 36). All patients had bilateral hearing restoration. The average auditory brainstem response threshold in the right (left) ear was >95 dB (>95 dB) in all patients at baseline, and the average auditory brainstem response threshold in the right (left) ear was restored to 58 dB (58 dB) in patient 1, 75 dB (85 dB) in patient 2, 55 dB (50 dB) in patient 3 at 26 weeks, and 75 dB (78 dB) in patient 4 and 63 dB (63 dB) in patient 5 at 13 weeks. The speech perception and the capability of sound source localization were restored in all five patients. These results provide preliminary insights on the safety and efficacy of binaural AAV gene therapy for hereditary deafness. The trial is ongoing with longer follow-up to confirm the safety and efficacy findings. Chinese Clinical Trial Registry registration: ChiCTR2200063181 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.G. is a staff member of Shanghai Refreshgene Therapeutics Co., Ltd. Z.-Y.C. is a cofounder of Salubritas Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Deafness and hearing loss.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (WHO, 2024).
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet392, 1789–1858 (2018). 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2020YFA0908201/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)
- 2023YFC2508400/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)
- 2021YFA1101302/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology)
- 82225014 and 82171148/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82192864/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

