Aggregation-resistant alpha-synuclein tetramers are reduced in the blood of Parkinson's patients
- PMID: 38839930
- PMCID: PMC11250827
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-024-00083-5
Aggregation-resistant alpha-synuclein tetramers are reduced in the blood of Parkinson's patients
Abstract
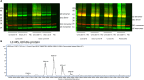
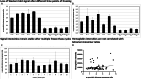
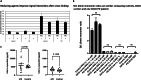
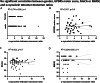
Synucleinopathies such as Parkinson's disease (PD) are defined by the accumulation and aggregation of the α-synuclein protein in neurons, glia and other tissues. We have previously shown that destabilization of α-synuclein tetramers is associated with familial PD due to SNCA mutations and demonstrated brain-region specific alterations of α-synuclein multimers in sporadic PD patients following the classical Braak spreading theory. In this study, we assessed relative levels of disordered and higher-ordered multimeric forms of cytosolic α-synuclein in blood from familial PD with G51D mutations and sporadic PD patients. We used an adapted in vitro-cross-linking protocol for human EDTA-whole blood. The relative levels of higher-ordered α-synuclein tetramers were diminished in blood from familial PD and sporadic PD patients compared to controls. Interestingly, the relative amount of α-synuclein tetramers was already decreased in asymptomatic G51D carriers, supporting the hypothesis that α-synuclein multimer destabilization precedes the development of clinical PD. Our data, therefore suggest that measuring α-synuclein tetramers in blood may have potential as a facile biomarker assay for early detection and quantitative tracking of PD progression.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Blood; Human; Parkinson’s disease; Tetramer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- n.a./Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen (DZNE)
- n.a./University Bonn
- n.a./University of Bonn
- n.a./Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- nU54,2xR01/US National Institute of Neurological Disorders
- n.a./Chan Zuckerberg Collaborative Pairs Initiative Phase 2
- R01 NS078165/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- PID2021-1265840A-100/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (MCIN)
- R01 NS109209/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- n.a./Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
- n.a./NIH UK
- U54 NS110435/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- n.a./Eisei pharmaceuticals
- n.a./ERDF
- n.a./Maria Zambrano Fellowship
- n.a./DRI
- 205167/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- n.a./Rosetrees Trust (Rosetrees)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

