Effect of flavonoids from grape seed and cranberry extracts on the microbiological activity of Streptococcus mutans: a systematic review of in vitro studies
- PMID: 38840232
- PMCID: PMC11155149
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04263-0
Effect of flavonoids from grape seed and cranberry extracts on the microbiological activity of Streptococcus mutans: a systematic review of in vitro studies
Abstract
Objective: To provide an overview of the available scientific evidence from in vitro studies regarding the effect induced by the flavonoids contained in grape seed extracts (GSE) and cranberry on the microbiological activity of Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans).
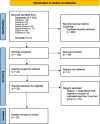
Methods: This systematic review was performed following the parameters of the PRISMA statement (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis). Electronic and manual searches were conducted using PubMed, ScienceDirect, Web of Science, EBSCO, and Cochrane databases. Reference lists of selected articles were reviewed to identify relevant studies. The search was not limited by year and was conducted solely in English. Eligible studies comprised publications describing in vitro studies that evaluated the effect of flavonoids derived from GSE and cranberry extracts on the microbiological activity of S. mutans. Common variables were identified to consolidate the data. Authors of this review independently screened search results, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias.
Results: Of the 420 studies identified from the different databases, 22 publications were finally selected for review. The risk of bias was low in 13 articles and moderate in 9. The studies analyzed in this review revealed that cranberry extract has an inhibitory effect on the bacterial growth of S. mutans in ranges from 0.5 mg/mL to 25 mg/mL, and GSE exerts a similar effect from 0.5 mg/mL to 250 mg/mL. Additionally, the extracts or their fractions showed reduced biofilm formation capacity, decreased polymicrobial biofilm biomass, deregulation of glycosyltransferases (Gtf) B and C expression, and buffering of pH drop. In addition to adequate antioxidant activity related to polyphenol content.
Conclusions: The overall results showed that the extracts of cranberry and grape seed were effective in reducing the virulence factors of the oral pathogen. According to the data, proanthocyanidins are the active components in cranberry and grape seed that effectively resist S. mutans. They can inhibit the formation of insoluble polysaccharides in the extracellular matrix and prevent glycan-mediated adhesion, cohesion, and aggregation of the proteins in S. mutans. This suggests that these natural extracts could play an important role in the prevention of cariogenic bacterial colonization, as well as induce a decrease in their microbiological activity.
Keywords: Streptococcus mutans; Cranberry; Dental caries; Grape seed extract; Proanthocyanidin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Machiulskiene V, Campus G, Carvalho JC, Dige I, Ekstrand KR, Jablonski-Momeni A, Maltz M, Manton DJ, Martignon S, Martinez-Mier EA, Pitts NB, Schulte AG, Splieth CH, Tenuta LMA, Ferreira Zandona A, Nyvad B. Terminology of dental caries and dental caries management: consensus report of a workshop organized by ORCA and cariology research group of IADR. Caries Res. 2020;54(1):7–14. doi: 10.1159/000503309. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases