Targeting mTOR and survivin concurrently potentiates radiation therapy in renal cell carcinoma by suppressing DNA damage repair and amplifying mitotic catastrophe
- PMID: 38840237
- PMCID: PMC11155143
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03079-8
Targeting mTOR and survivin concurrently potentiates radiation therapy in renal cell carcinoma by suppressing DNA damage repair and amplifying mitotic catastrophe
Abstract
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) was historically considered to be less responsive to radiation therapy (RT) compared to other cancer indications. However, advancements in precision high-dose radiation delivery through single-fraction and multi-fraction stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) have led to better outcomes and reduced treatment-related toxicities, sparking renewed interest in using RT to treat RCC. Moreover, numerous studies have revealed that certain therapeutic agents including chemotherapies can increase the sensitivity of tumors to RT, leading to a growing interest in combining these treatments. Here, we developed a rational combination of two radiosensitizers in a tumor-targeted liposomal formulation for augmenting RT in RCC. The objective of this study is to assess the efficacy of a tumor-targeted liposomal formulation combining the mTOR inhibitor everolimus (E) with the survivin inhibitor YM155 (Y) in enhancing the sensitivity of RCC tumors to radiation.
Experimental design: We slightly modified our previously published tumor-targeted liposomal formulation to develop a rational combination of E and Y in a single liposomal formulation (EY-L) and assessed its efficacy in RCC cell lines in vitro and in RCC tumors in vivo. We further investigated how well EY-L sensitizes RCC cell lines and tumors toward radiation and explored the underlying mechanism of radiosensitization.
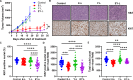
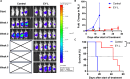
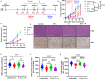
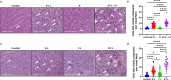
Results: EY-L outperformed the corresponding single drug-loaded formulations E-L and Y-L in terms of containing primary tumor growth and improving survival in an immunocompetent syngeneic mouse model of RCC. EY-L also exhibited significantly higher sensitization of RCC cells towards radiation in vitro than E-L and Y-L. Additionally, EY-L sensitized RCC tumors towards radiation therapy in xenograft and murine RCC models. EY-L mediated induction of mitotic catastrophe via downregulation of multiple cell cycle checkpoints and DNA damage repair pathways could be responsible for the augmentation of radiation therapy.
Conclusion: Taken together, our study demonstrated the efficacy of a strategic combination therapy in sensitizing RCC to radiation therapy via inhibition of DNA damage repair and a substantial increase in mitotic catastrophe. This combination therapy may find its use in the augmentation of radiation therapy during the treatment of RCC patients.
Keywords: Mitotic catastrophe; Radiation therapy; Renal cancer; Survivin; mTOR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DM, VSM, and KP have applied for the protection of intellectual property for the tumor-targeted liposomal formulation described in the manuscript. There are no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Update of
-
Targeting mTOR and Survivin Concurrently Potentiates Radiation Therapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing DNA Damage Repair and Amplifying Mitotic Catastrophe.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 23:rs.3.rs-3770403. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3770403/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 6;43(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03079-8. PMID: 38196607 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

