Primary tooth aspiration during conscious sedation with N2O: foreign body removal with rigid bronchoscopy
- PMID: 38840645
- PMCID: PMC11148418
- DOI: 10.17245/jdapm.2024.24.3.205
Primary tooth aspiration during conscious sedation with N2O: foreign body removal with rigid bronchoscopy
Abstract
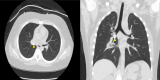
A 7-year-old girl visited the Samsung Medical Center emergency room for primary tooth aspiration during primary tooth extraction under conscious sedation with N2O. The patient showed no signs of respiratory complications. Chest radiography and CT revealed a tooth in the right bronchi. Foreign body removal using rigid bronchoscopy was performed on the day of aspiration. With close monitoring of the airway in the pediatric ICU, extubation was performed the next day, and the patient was discharged the same day. The primary objective of this case report was to highlight the potential risk of aspiration associated with the use of N2O gas for conscious sedation.
Keywords: Aspiration; Conscious Sedation; Foreign Bodies; Removal.
Copyright © 2024 Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATIONS OF INTEREST: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Treatment of bronchial foreign body aspiration with extracorporeal life support in a child: A case report and literature review.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;94:82-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.01.011. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28167019 Review.
-
Endoscopic removal of an aspirated healing abutment and screwdriver under conscious sedation.Implant Dent. 2014 Jun;23(3):250-2. doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000100. Implant Dent. 2014. PMID: 24819812
-
Foreign body extraction through the rigid bronchoscopy.Vojnosanit Pregl. 2011 Oct;68(10):878-80. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2011. PMID: 22165755
-
An alternative method of management of pediatric airway foreign bodies in the absence of rigid bronchoscopy.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Apr;77(4):480-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.12.010. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23294930
-
Diagnostic value of various investigations in children with suspected foreign body aspiration: review.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2011 Nov;128(5):248-52. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2010.12.011. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2011. PMID: 22018977 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

