Graft Position, Healing, and Resorption in Anterior Glenohumeral Instability: A Comparison of 4 Glenoid Augmentation Techniques
- PMID: 38840788
- PMCID: PMC11151773
- DOI: 10.1177/23259671241253163
Graft Position, Healing, and Resorption in Anterior Glenohumeral Instability: A Comparison of 4 Glenoid Augmentation Techniques
Abstract
Background: The success of glenoid augmentation procedures depends on accurate placement and healing of the graft to the glenoid. Different glenoid augmentation techniques have been described, but no comparative studies between them exist.
Purpose: To assess the bone graft position, healing, and resorption in a group of patients treated with 1 of 4 procedures: arthroscopic anterior bone-block procedure using either (1) fresh-frozen iliac crest allograft or (2) iliac crest autograft, (3) open Latarjet, or (4) arthroscopic Latarjet.
Study design: Cohort study; Level of evidence, 3.
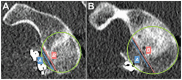
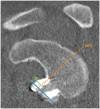
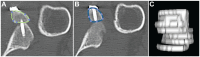
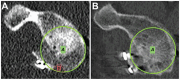
Methods: A total of 40 patients (87.5% men; mean age, 29.5 ± 7.9 years) were included, with 10 patients in each of the procedure groups. The graft position in the axial and sagittal planes was assessed on postoperative computed tomography (CT). Graft healing and resorption were assessed in a second CT scan performed 1 year postoperatively. Qualitative variables were compared between the 4 procedures using the chi-square test, and quantitative variables were compared with the Student t test or Mann-Whitney U test.
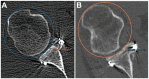
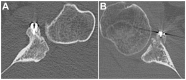
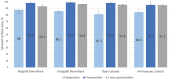
Results: No differences were found between the procedures in the axial or sagittal position. The healing rate was significantly lower in the allograft bone-block group (20%) compared with the autograft bone-block (80%), open Latarjet (90%), and arthroscopic Latarjet (90%) groups (P < .001). Graft resorption developed in 17 of 40 (42.5%) cases overall. Osteolysis occurred in 100% of cases in the allograft bone-block group compared with 50% in the autograft group, 20% in the open Latarjet group, and 0% in the arthroscopic Latarjet group (P < .001). The glenoid surface area on 1-year CT scan was significantly lower in the allograft bone-block group compared with the autograft bone-block, open Latarjet, and arthroscopic Latarjet groups (P < .001).
Conclusion: Arthroscopic bone-block, open Latarjet, and arthroscopic Latarjet procedures provided accurate bone graft positioning. However, very high rates of osteolysis and nonunion were observed in the iliac crest fresh-frozen allograft bone-block procedure when compared with the other procedures.
Keywords: Latarjet procedure; anterior shoulder instability; arthroscopic bone block; glenoid bone loss.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest in the authorship and publication of this contribution. AOSSM checks author disclosures against the Open Payments Database (OPD). AOSSM has not conducted an independent investigation on the OPD and disclaims any liability or responsibility relating thereto. Ethical approval for this study was obtained from Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal (protocol No. 0.92, approved under Act 400).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiographic Analysis of Glenoid Size and Shape After Arthroscopic Coracoid Autograft Versus Distal Tibial Allograft in the Treatment of Anterior Shoulder Instability.Am J Sports Med. 2018 Sep;46(11):2717-2724. doi: 10.1177/0363546518789348. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Am J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 30095986
-
Normalization of glenohumeral articular contact pressures after Latarjet or iliac crest bone-grafting.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Jun;92(6):1478-89. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.I.00220. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010. PMID: 20516324
-
Outcomes of an anterior bone block technique with iliac crest allograft for the management of anteroinferior shoulder instability with subcritical glenoid defects.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025 Mar 19:S1058-2746(25)00242-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2025.02.022. Online ahead of print. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025. PMID: 40118439
-
Outcomes are comparable using free bone block autografts versus allografts for the management of anterior shoulder instability with glenoid bone loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis of "The Non-Latarjet".Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Jul;29(7):2159-2174. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06194-z. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32749510
-
Outcomes of the Latarjet Procedure Versus Free Bone Block Procedures for Anterior Shoulder Instability: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Mar;49(3):805-816. doi: 10.1177/0363546520925833. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 32795174
References
-
- Allain J, Goutallier D, Glorion C. Long-term results of the Latarjet procedure for the treatment of anterior instability of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(6):841-852. - PubMed
-
- Barth J, Neyton L, Metais P, et al.. Is the two-dimensional computed tomography scan analysis reliable for coracoid graft positioning in Latarjet procedures? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(8):e237-e242. - PubMed
-
- Baudi P, Righi P, Bolognesi D, et al.. How to identify and calculate glenoid bone deficit. Chir Organi Mov. 2005;90(2):145-152. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia S, Frank RM, Ghodadra NS, et al.. The outcomes and surgical techniques of the Latarjet procedure. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(2):227-235. - PubMed
-
- Boehm E, Minkus M, Moroder P, Scheibel M. Massive graft resorption after iliac crest allograft reconstruction for glenoid bone loss in recurrent anterior shoulder instability. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(7):895-903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

