Characterization of the key flavor compounds in cream cheese by GC-MS, GC-IMS, sensory analysis and multivariable statistics
- PMID: 38840807
- PMCID: PMC11150910
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100772
Characterization of the key flavor compounds in cream cheese by GC-MS, GC-IMS, sensory analysis and multivariable statistics
Abstract
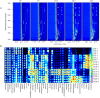
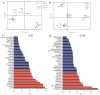
The aroma types of cream cheese affect its commercial value and consumer acceptability. However, the types of volatile substances and sensory characteristics of cream cheese at different fermentation stages are still unclear. Therefore, in this study, headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) and headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) were used to analyze the volatile substances in cream cheese fermentation. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), odor activity value (OAV), relative odor activity value (ROAV) and variable projection importance (VIP) were used to identify the characteristic flavor substances in cream cheese fermentation. Finally, the relationship between key flavor substances and sensory characteristics was determined by partial least squares (PLS) analysis. A total of 34 and 36 volatile organic compounds were identified by HS-SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-MS, respectively, and 14 characteristic flavor substances were found, based on VIP, ROAV and OAV models. Combined with sensory analysis and flavor substance changes, it was found that the cream cheese fermented for 15 d had the best flavor and taste. This study reveals the characteristics and contribution of volatile substances in cream cheese at different fermentation stages, which provides new insights into improving flavor and quality control.
Keywords: Cream cheese; Flavor substances; Gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry; Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; Multivariate statistics.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Discrimination and characterization of the volatile profiles of five Fu brick teas from different manufacturing regions by using HS-SPME/GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS.Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Sep 25;5:1788-1807. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.09.024. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36268133 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the flavor profile and dynamic changes in Chinese traditional fish sauce (Yu-lu) based on electronic nose, SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS.Food Res Int. 2024 Sep;192:114772. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114772. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39147494
-
Flavor Characteristics of Different Varieties of Flue-Cured Tobacco Based on Headspace Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry and Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry.ACS Omega. 2025 May 16;10(20):20382-20401. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00343. eCollection 2025 May 27. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40454082 Free PMC article.
-
Feature selection and extraction strategies for non-targeted analysis using GC-MS and GC-IMS: A tutorial.Anal Chim Acta. 2025 Mar 15;1343:343635. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2025.343635. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Anal Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 39947788 Review.
-
Recent trends in the chromatographic analysis of volatile flavor and fragrance compounds: Annual review 2020.Anal Sci Adv. 2021 Feb 4;2(3-4):157-170. doi: 10.1002/ansa.202000158. eCollection 2021 Apr. Anal Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 38716458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-targeted metabolomics reveals the effects of fermented methods on the flavor, quality, and metabolites of whipping cream.Food Chem X. 2025 Mar 15;27:102376. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102376. eCollection 2025 Apr. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40191846 Free PMC article.
-
Process optimization and flavor characteristics of cream cheese fermented with avocado co-cultures.Food Chem X. 2025 Jul 7;29:102745. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102745. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40686872 Free PMC article.
-
Formation Mechanism of Lipid and Flavor of Lard Under the Intervention of Heating Temperature via UPLC-TOF-MS/MS with OPLS-DA and HS-GC-IMS Analysis.Foods. 2025 Jul 11;14(14):2441. doi: 10.3390/foods14142441. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724262 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Plant-Based Milks Based on Chestnut and Soybean: Comprehensive Evaluation of Fermentation Characteristics and Aroma Profiles Using Four Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains.Foods. 2025 Jul 17;14(14):2511. doi: 10.3390/foods14142511. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724329 Free PMC article.
-
Stretching Profile Correlated With the Aromatic Properties of Aged Light Cheese Enriched With Milk Globule Membrane Components.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 May 25;13(6):e70330. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70330. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40444132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Dalali S., Zheng F., Sun B., Rahman T., Chen F. Tracking volatile flavor changes during two years of aging of Chinese vinegar by HS-SPME-GC-MS and GC-O. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022;106 doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104295. - DOI
-
- Alewijn M., Smit B.A., Sliwinski E.L., Wouters J.T.M. The formation mechanism of lactones in Gouda cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2007;17(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2006.01.002. - DOI
-
- Amaral J.B.S., Grisi C.V.B., Vieira E.A., Ferreira P.S., Rodrigues C.G., Diniz N.C.M., Cordeiro A.M. T.d.M. Light cream cheese spread of goat milk enriched with phytosterols: physicochemical, rheological, and microbiological characterization. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. (Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft -Technol.) 2022;157 doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113103. - DOI
-
- Caron T., Piver M.L., Peron A.C., Lieben P., Lavigne R., Brunel S., Chassard C. Strong effect of Penicillium roqueforti populations on volatile and metabolic compounds responsible for aromas, flavor and texture in blue cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021;354 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109174. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

