Cellular interactions and microenvironment dynamics in skeletal muscle regeneration and disease
- PMID: 38840849
- PMCID: PMC11150574
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1385399
Cellular interactions and microenvironment dynamics in skeletal muscle regeneration and disease
Abstract
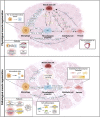
Skeletal muscle regeneration relies on the intricate interplay of various cell populations within the muscle niche-an environment crucial for regulating the behavior of muscle stem cells (MuSCs) and ensuring postnatal tissue maintenance and regeneration. This review delves into the dynamic interactions among key players of this process, including MuSCs, macrophages (MPs), fibro-adipogenic progenitors (FAPs), endothelial cells (ECs), and pericytes (PCs), each assuming pivotal roles in orchestrating homeostasis and regeneration. Dysfunctions in these interactions can lead not only to pathological conditions but also exacerbate muscular dystrophies. The exploration of cellular and molecular crosstalk among these populations in both physiological and dystrophic conditions provides insights into the multifaceted communication networks governing muscle regeneration. Furthermore, this review discusses emerging strategies to modulate the muscle-regenerating niche, presenting a comprehensive overview of current understanding and innovative approaches.
Keywords: endothelial cells; fibro-adipogenic progenitors; macrophages; muscle niche dynamics; muscle stem cells; muscular dystrophies; regenerative medicine strategies; skeletal muscle regeneration.
Copyright © 2024 Rodríguez, Timóteo-Ferreira, Minchiotti, Brunelli and Guardiola.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

